I. Introduction
KYC regulations allude to the rules organizations and financial establishments should keep to confirm the identity, sustainability, and hazard of a potential or existing client. To stop money laundering in the US (United States) an act was passed in 1970 called as Bank Secrecy Act (BSA). The main goal of this act is to recognize activities such as money laundering.
KYC rules and regulations vary in areas such as different countries and states and modify guidelines according to their requirement. Globally KYC supported common principles and elements. The integrity of the financial system is maintained and criminal activity taking place in an organization is controlled by KYC regulations. Sensitive client information is handled by the organizations and reported to the concerned authorities if any suspicious activity takes place. The digital footprint proactive approach helps the institution battle financial crimes and other suspicious activities
KYC has many purposes but some of its main objectives are;
- It helps in lowering the probability of crime related to finances as organizations take guarantees of the identity and background of clients.
- Secondly, it helps in identifying suspicious activities and transactions that are not legitimate.
- Lastly, it helps prevention of money laundering. KYC system plays a crucial role in business organizations and its regulations help in protecting criminal activities. KYC also helps businesses to establish regulatory requirements with the government.
Also Read: What is a Digital Footprint in KYC?
II.Key Components of KYC Regulations
Identification and verification of customers
The initial step is the identification of the customer, which is gathering accurate information about clients’ identity using reliable data sources or documents. Regularly, the client’s name, address, and date of birth are collected as a component of the KYC cycle.
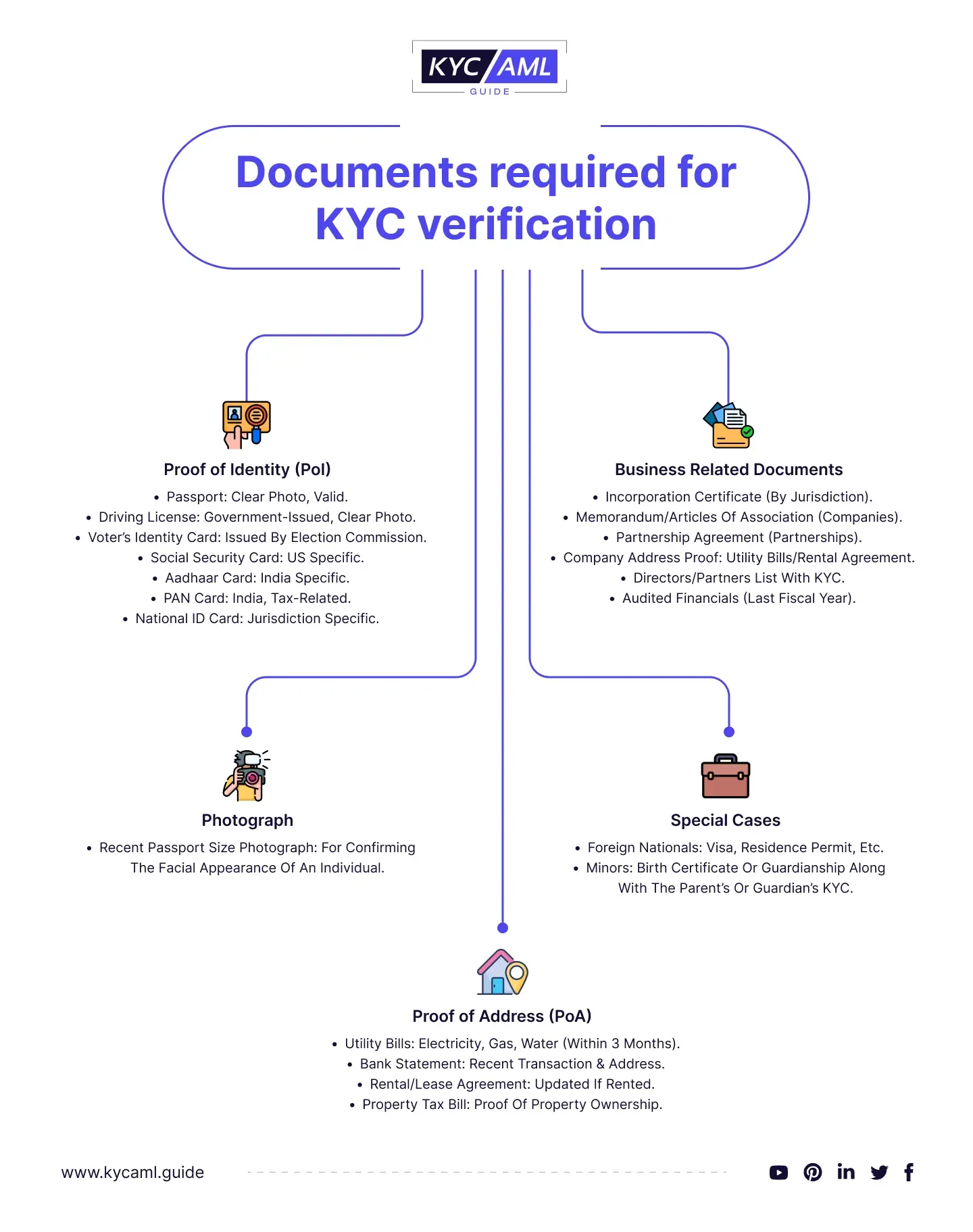
Businesses verify KYC information in a variety of ways to ensure its accuracy and dependability. Document verification includes approving identity documents such as passports, driver’s licenses, or national identity cards to verify the customer’s identity. KYC identity verification includes biometric, facial recognition, two-factor, and knowledge-based authentication, as well as one-time password (OTP) authentication.
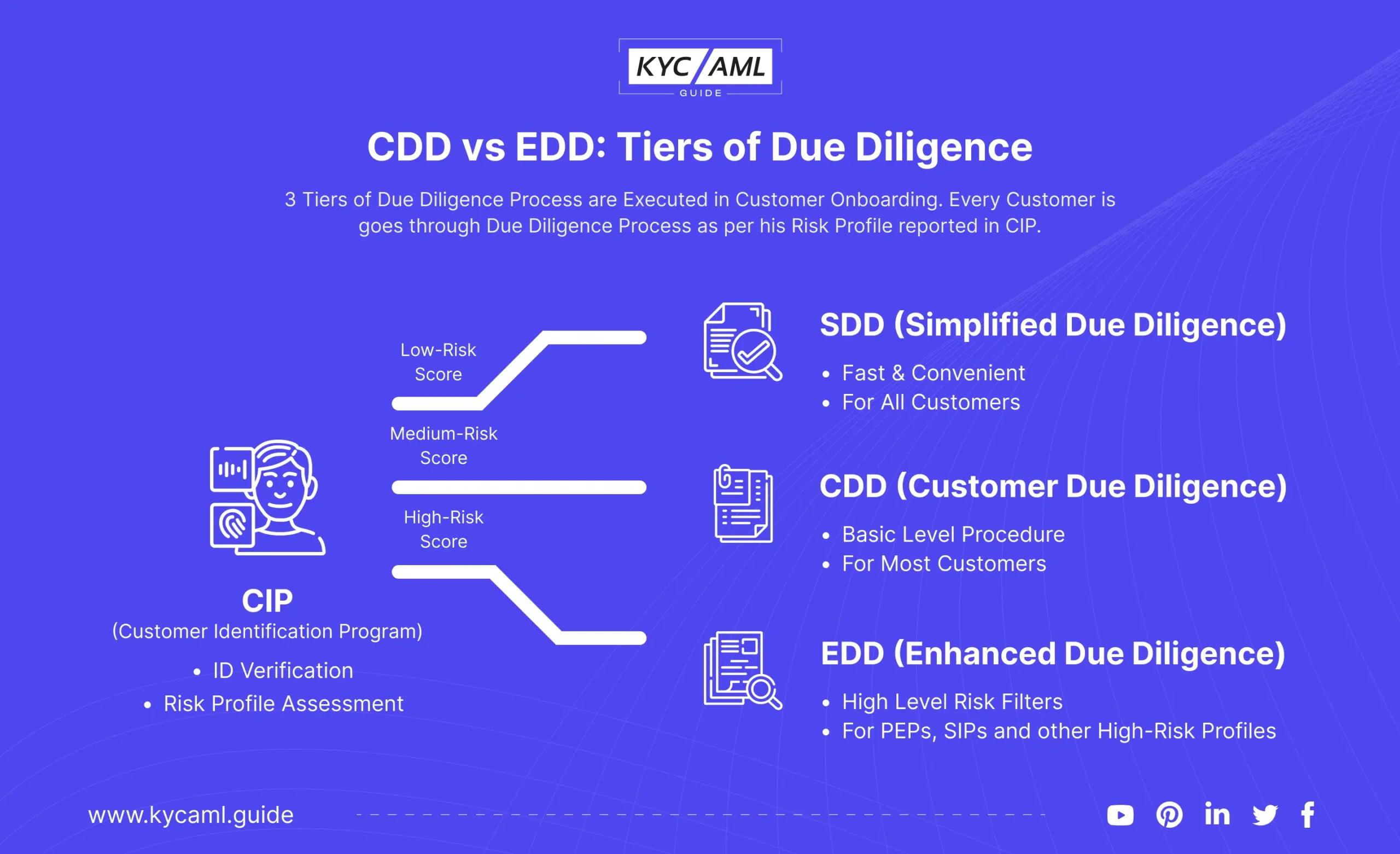
Risk assessment and due diligence
Similarly, risk assessment strategies are used to overview a client’s risk profile as a result of factors like their involvement in criminal tasks, reputation, or financial history.

Customer due diligence (CDD) involves assessing the risks associated with each customer and determining the level of controls required. Together, these techniques provide a solid foundation for compelling customer verification in the KYC cycle. This includes looking at the customer’s past, their finances, and any potential risk. Organizations should conduct detailed investigations, through Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for high-risk clients, for example, getting extra documents or information about the client’s financial history and performance.
Ongoing monitoring of customer activities
The third component is ongoing monitoring, which constantly monitors customer accounts and transactions to identify suspicious or anomalous activity that may occur over time. It consists of several components, including:
Record-keeping and reporting obligations
Companies need secure and accessible data to demonstrate how much control compliance teams have over the onboarding process. This data is the essential audit trail for any money laundering or terrorist financing investigation. For all types of businesses, there are no set record-keeping requirements, there should be sufficient documentation to support a company’s onboarding process. To demonstrate why a particular client was hired and what steps they went through. How long companies must keep this information depends on local laws and regulations.
Companies must report suspicious activity to the appropriate authorities depending on the jurisdiction, such as the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) or the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU).
III. Industries Affected by KYC Regulations
KYC is relevant to many companies and industries. Anyone offering goods or services and conducting financial transactions should consider the importance of KYC regulations. This is why the following industries are most affected by KYC practices:

Banking and financial institutions
People or organizations are normally expected to go through KYC regulations when they need to open a new bank account, apply for a credit card, or establish a relationship with a financial institution. The institution can determine the client’s risk and who it is dealing with as a result of this. To meet regulatory requirements and prevent financial crimes, financial institutions and banks implement KYC regulations.
KYC is required for certain high-value financial transactions, for example, bank transfers, money trades, or large cash deposits. This aids in the prevention of money laundering and the illegal movement of funds.
Insurance companies
People are expected to give KYC documentation while taking out insurance. This is fundamental for acknowledgment and to prevent insurance fraud.
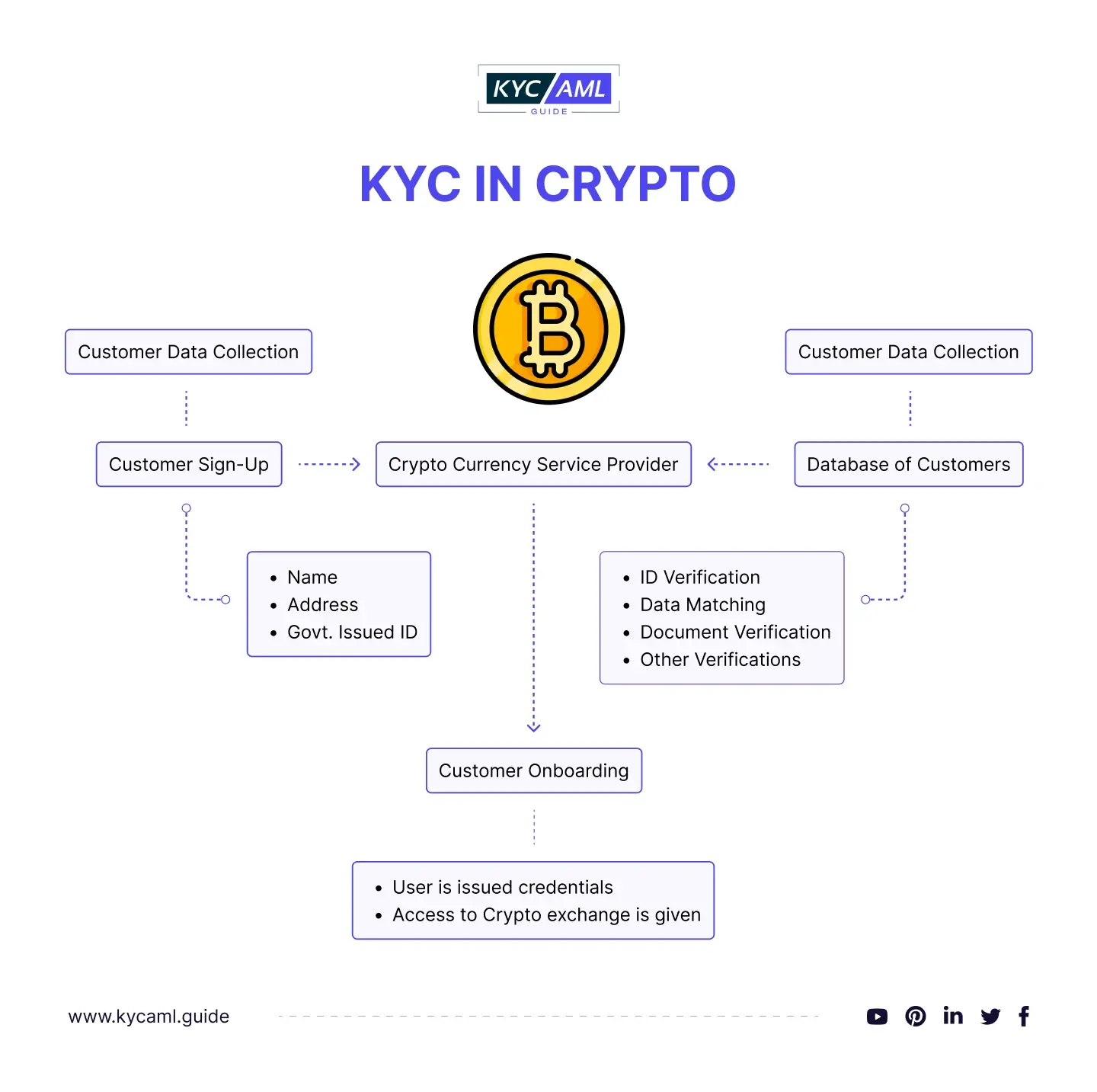
Cryptocurrency exchanges
Online services, such as cryptocurrency exchanges also require KYC regulations as part of customer onboarding. Its purpose is to comply with legal regulations and reduce the risk of financial crimes.
Real estate sector
KYC regulations are required for real estate transactions In some jurisdictions, especially high-value real estate. This is to ensure that the source of the money is legitimate and to prevent money laundering through real estate purchases.

Gaming and Gambling Industry
The online gambling industry is growing rapidly. It is expected to reach over $94 billion by 2024. Online gambling establishments must verify the identity of their customers, including age address verification, and risk profiles. The idea behind KYC for online gambling and gaming sites is to prevent bad actors, including fraud, and prevent minors from accessing age-restricted platforms.
Non-profit organizations
The FATF recommends that countries encourage non-profit organizations to:
- Apply best financial accounting and understand donor verification, development, and documentation practices
- Money transfers using formal financial systems
- Conduct audits and due diligence for partners, field operations, and overseas
IV. Benefits of KYC Regulations
KYC regulations have the following key benefits in today’s business world:
- Prevent and reduce fraud resulting from false identity or online fraud
- Prevention of money laundering
- Help lenders properly risk-assess customers by identifying their financial history and the assets they hold
- This creates trust between customers and organizations, which attracts more investment to a country.
- Protects customer accounts from unauthorized access by third parties
- Overall business growth due to less financial crime leads
V. Challenges of KYC Regulations
Common challenges companies face for KYC regulations include:
- Low conversion rates
- High onboarding costs
- Poor record keeping
- Compliance costs
- Lengthy onboarding processes
- Wasting time and money on false positives
- Inability to detect changes in circumstances
- Volume of Documents
VI. Conclusion
KYC regulations have evolved essentially throughout the years worldwide to address money laundering and evolving dangers. KYC regulations have become more complex and severe starting from the presentation of the FATF recommendations in 1990 and the execution of the EU anti-money laundering legislation. As money laundering avoidance turns out to be more complicated and modern, we anticipate that KYC regulations should keep on advancing, alongside innovations and strategies for identity verification and risk assessment. To comply with these ever-changing laws, businesses must remain vigilant and adapt.
One of the greatest difficulties for KYC compliance in 2024 is keeping up with the evolving guidelines. As we have seen, KYC regulations are continually refreshed to address new dangers and difficulties. This indicates that it is essential for businesses to be aware of these modifications, to adjust their compliance programs following them, and to make certain that they comply with the new requirements.
organizations can adopt a risk-based approach to KYC consistency compliance to overcome these difficulties. Furthermore, organizations can utilize technologies and tools, for example, AI and ML to break down customer data and identify suspicious activity successfully.





