Difference Between CDD and EDD
Look at the Diagram below to understand the three tiers of Due Diligence: Firstly, there are three stages of Due Diligence in the KYC Onboarding Process. Before Due Diligence, there is a process called Customer Identification Program (CIP). In CIP, the customer’s ID verification is done to generate an initial Risk Profile, and a Risk Score is given to the client. Hence, based on the Risk Profile and Risk Score, the Due Diligence process is carried out as shown in the chart.
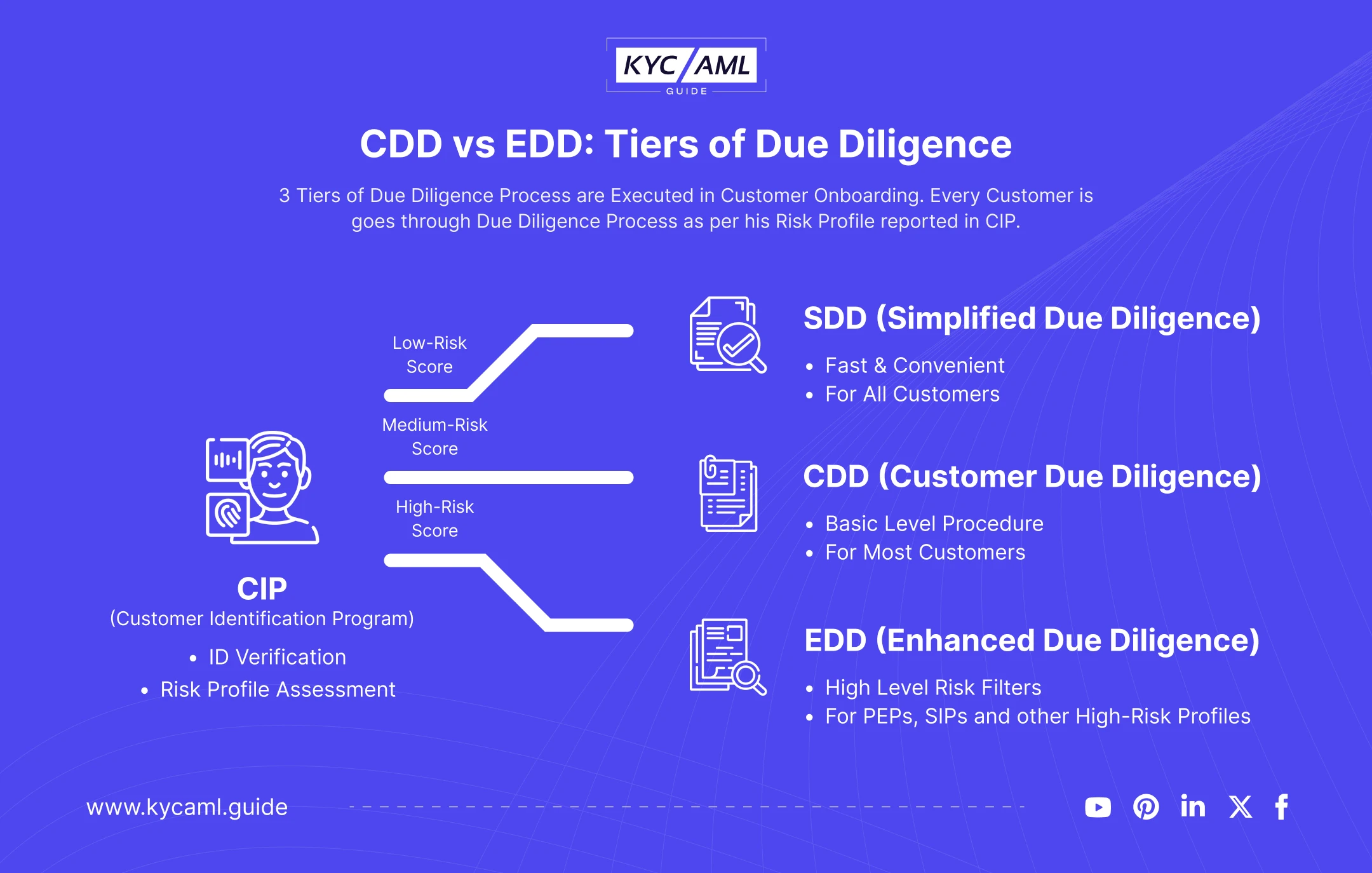
Simplified Due Diligence (SDD)
When the risk score is low and the customer is identified as a low-risk client. He is processed through a simplified Due Diligence procedure covering the initial level of risk monitoring. Since the customer poses no threat of Money Laundering or Terrorism Funding, he is easily onboarded.
Also Read: Due Diligence Checklist 2023: A Guide To Ensure AML Compliance
What is CDD in KYC?
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is the second tier of the due diligence process. Mostly, the medium risk profiles are scrutinized in this tier. Mostly, wealthy customers who are not considered PEPs are checked in CDD. Comparatively, CDD is more stringent than SDD in a risk-based KYC onboarding process.
What is EDD in KYC?
Now, the third and crucial tier is Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD). In this stage, the high-risk profiles are filtered. Mostly, the criminals are identified in this stage. This tier is introduced to highlight the PEPs (Politically Exposed Persons) and SIPs (Special Interest Persons). If the client is proven to have a criminal background or is on the sanction list, he is reported to the authorities.
Accordingly, there are seven aspects from which we shall compare CDD vs EDD.
Comparison of Customer Due Diligence vs Enhanced Due Diligence:
| Aspect | Customer Due Diligence (CDD) | Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) |
| Definition | CDD is a due diligence process carried out for normal risk-level clients. | EDD is a thorough and in-depth risk filter check for the high-risk profiles of clients. |
| Purpose | CDD is done to assess the normal risk customers and ensure a risk-free customer is onboarded at a normal level. | EDD requires in-depth information deep filters and risk checks to scrutinize PEPs, SIPs, and other high-risk clients. Also, EDD is done for clients with complex ownership structures (UBOs). |
| Scope | Normally, CDD is applied to every customer with a normal risk level. It includes the verification of ID documents such as Passports, ID Cards, Driver’s Licenses, etc. | Relatively, EDD is more strict and carries an in-depth check by verifying the details of a high-risk person. In addition to the CDD checklist, it verifies the wealth, interests, UBO ship, and sources of funds respectively. |
| Timing | Typically, CDD is carried out during the client’s onboarding where the risk posed by the client is normal. | EDD is mostly carried out when a high-risk client is identified or a Red Flag is raised. |
| Documents | Client identification Documents like Proof of ID, Proof of Address, etc. | the Client’s business registration details, financial statements, and sources of funds. |
| Procedures | Mostly, CDD is carried out for all customers. | Specifically, EDD is carried out for high-risk customers (PEPs and SIPs). |
| Effectiveness | It can only detect complex Money Laundering schemes or identify high-risk clients. | In contrast, EDD is able to identify Money Launderers at complex levels and it can be costly as well as time-consuming. |
Customer Due Diligence vs Enhanced Due Diligence: Which is better?
Overall, the notion of Customer Due Diligence vs Enhanced Due Diligence really depends on the specific risk profile of the customer. Largely, CDD is sufficient but for high-risk customers or Red Flags, EDD is conducted to mitigate the risks. Generally, it’s best to use a risk-based approach to due diligence. Hence, the level of due diligence should be based on the level of risk posed by the customer. Also, it is indifferent to compare CDD vs EDD in terms of preference.
CDD vs EDD in the UK and the US
CDD in the UK and the US
While Customer Due Diligence in the UK is regulated through the AML Directives till the event of Brexit. Hence, the UK is no longer subjected to comply with the EU-issued AMLD including the 6th AMLD. Instead, Anti-Money Laundering regulations in the UK are now directed by their domestic authorities. However, there is still a significant influence of FATF recommendations as the UK is still an active FATF member. Likewise, the FCA now governs the KYC and AML regulations in the UK.
Similarly, in the US, the Customer Due Diligence requirements are more or less the same as in the UK. But the risk-based approach might differ in documentary and non-documentary or both methods. Also, entities might require information like account type, transaction type, and other factors that normally occur in a transaction.
EDD in the UK and the US
Now, in the case of Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD), the process becomes more complex. Just as the risk level becomes high for a specific client, an alarm is raised and CDD is no longer sufficient. Now, the EDD is carried out to check the trails of finances and other suspicious activities deeply. Both in the UK and the US, Enhanced Due Diligence requires additional and stringent risk filters for high-risk clients like PEPs or SIPs.
Therefore, Customer Due Diligence vs Enhanced Due Diligence remains the same in the UK and the US. Thus, some regulatory authorities and bodies are monitoring firms’ risk levels in CDD and EDD.
Final Brief
On the whole, CDD and EDD are both important for a firm’s security and AML compliance. Comparatively, EDD is complex and costs more than CDD. But this cost saves the firm from the catastrophe of being sanctioned or banned due to Money Laundering. Customer trust is built when the system is risk-free and seamless at the same time. To achieve such compliance, KYC AML Guide is a handy tool to stay updated with the latest developments in CDD vs EDD. Lastly, it is important for firms to note their country’s regulatory framework. Accordingly, their Due Diligence processes shall be designed.





