Key Facts about Money Laundering
Here are some Money Laundering facts that show how much this illicit activity has crept into our financial system.
- Research shows that $300 billion is laundered through the United States of America every year.
- Criminals & Drug Paddlers launder $ 800 million to $ 2 trillion each year.
- Money Laundering costs around 2 to 5% of the world’s total GDP.
- In the US, Money Laundering totals 15-38% of global Money Laundering.
- 90% of Money Laundering activities go unidentified.
Also Read: Biggest Money Laundering Scandals 2023
Overview of Money Laundering
Before diving into the actual topic, let’s take a look at the prime definition of money laundering.
Firstly, you should understand that Money Laundering is a punishable crime and an illegal activity globally. Ideally, no country supports or legalizes Money Laundering. Money Laundering is a process by which criminals turn their black money into white money. As the name suggests, Laundering is a process of cleaning or washing clothes. Similarly, there are transactions and hidden financial procedures that convert illegal money into legalized money.
Process of Money Laundering
Learn how FINCEN defines Money Laundering here. According to this definition, money laundering is a major source of funding for criminal activities. It disguises illegal financial assets so that they become undetectable and can be used as legal money anywhere.
Money Laundering Cycle
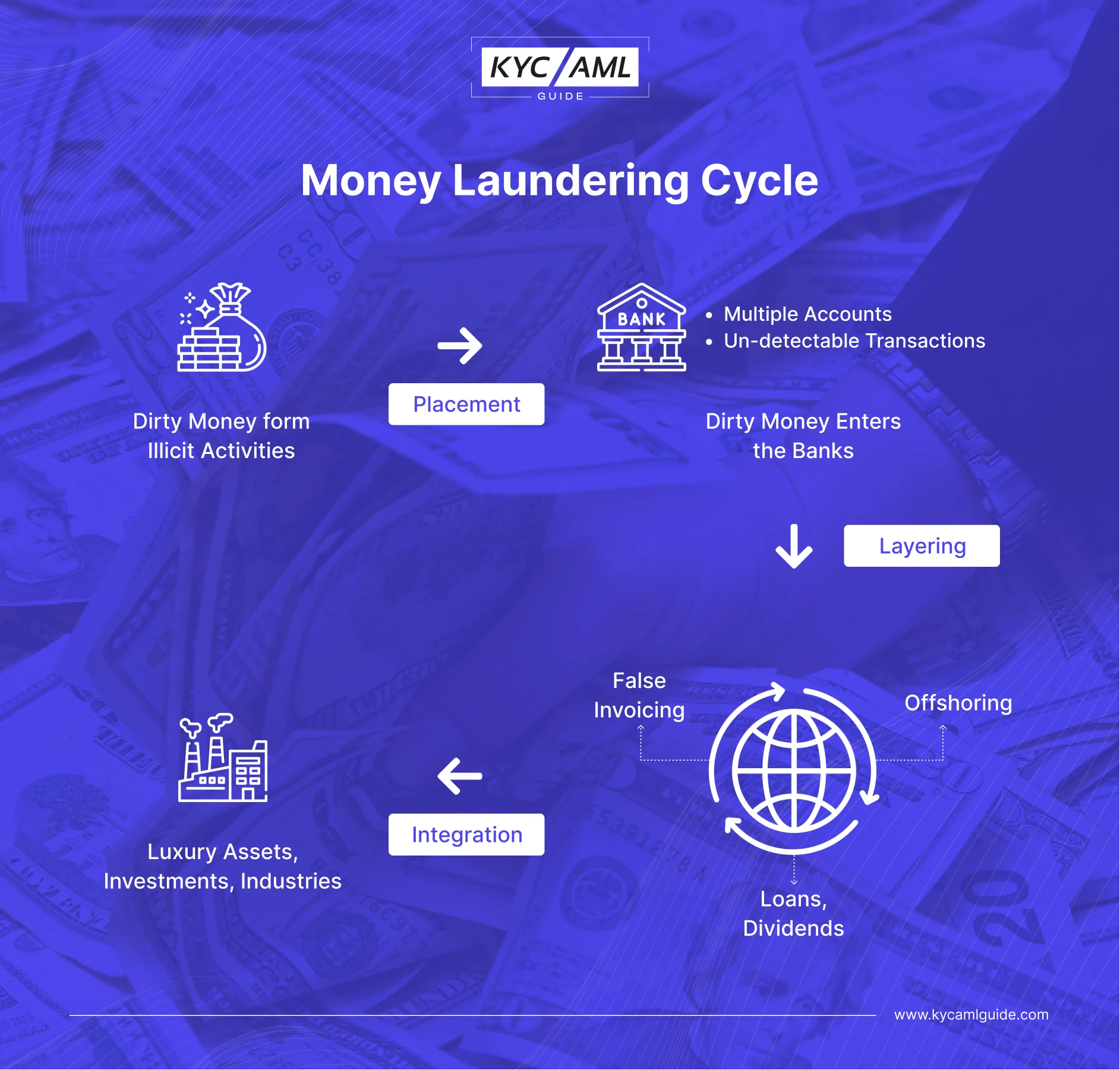
Primarily, it is a process through which crime-earned money is brought into the legal financial system. The 3 Money Laundering stages are explained below:
1 Money Laundering Placement
The first stage of the money laundering process is the placement of Money itself. Here, illegal funds penetrate the legal financial and economic cycle. Any coverup business or cash is registered and deposited in the bank. Tactfully, these transactions are kept small enough to appear non-suspicious and non-risky.
The placement of Money is done through different entities and various procedures. Some of them are listed below:
Cash through business
Cash is added in a legitimate circle through businesses with minor to zero variable costs. These businesses include car parks, car washes, etc.
False Invoicing
It is inserting fake invoices that match the cash flows. This looks like a settlement or a legal payment against some purchase or expense.
Smurfing
Storing or recording small amounts of cash that go undetected by AML activities in the bank accounts or credit cards. This cash is then used to pay expenses or for unauthorized payments. Smurfing is difficult to detect and a very common technique in Money laundering.
Offshore companies & Trusts
This hides the real owner’s identity and liability is shifted to a smear name that might not exist in reality.
Foreign Bank Account
Physically, transporting small amounts of cash legally or illegally and depositing it in foreign accounts. Afterward sending this money to the home country account.
Halted/Aborted Transaction
A legal professional or an accountant is involved in holding the client’s account. The proposed transaction through this account is canceled and funds are returned from an undetected source
2 Layering of Money
The second stage in the 3 stages of Money Laundering is called Layering. It refers to the separation of funds/money from the source. In the Money Laundering Placement stage, the funds can still be tracked to the head of funds. Hence, layering is required which can have further stages. Simply, layering covers the tracks by adding more transactions, and procedures making it difficult to track. Anti-money laundering authorities need help to reach the exact source of Launderers if the layering is done correctly. So, the more layers are added, the more difficult it is to track the source.
Moreover, Financial assets, real estate, and other complicated businesses are used for Layering in Money Laundering. Criminals invest their money into a layer of legitimate business activities for diversifying their funds. This makes it difficult for the regulators to track due to multiple layers.
3 Integration of Funds
Finally, the funds are integrated where money is cleaned and legalized. Effectively, it appears legitimate and is usable anywhere legally. This is the final stage of the 3 stages of Money Laundering. Also, it is done by being undercover so that law enforcement doesn’t get notified. Keeping a low profile is another technique while integrating money laundering. The Money Launderers often include payrolls & other taxes to wash out their money. So, they get nearly 50% leverage for ‘shrinkage’.
Some methods of integration in Money laundering are listed below:
- Fake Payrolls: For payrolls, employees are paid through the accounts. Sometimes fake employees are shown in statements. Mostly, the deductions from employees’ salaries are also a part of the integration.
- Lending to Shareholders or BoDs: These loans are never repaid as per the source.
- Dividends: criminals pay dividends to the shareholders of companies.
Money Laundering Schemes
Basically, the types of money laundering are the schemes. Commonly, 6 schemes of Money Laundering are famous that facilitate Money Laundering. From Money Laundering Placement to Integration, the schemes carry out all the 3 Stages of Money Laundering.
Following are the 6 schemes of Money Laundering:
Structuring & Smurfing
In this process, the Launderers split the funds into smaller amounts so that the transactions appear non-suspicious. Normally, FIs are obliged to report any transaction equal to or greater than $10000. So, depositing a larger sum of money can raise an alarm for regulators and law enforcement. Through enlisting in multiple countries for the help of friends, relatives, and other related parties. Relatively, these parties are trustworthy to the money launderer for smurfing.
Know the Difference Between Smurfing and Structuring | KYC AML Guide
Round Tripping
Commonly, shell companies, individuals & multiple accounts are used for round-tripping. It is similar to the layering process.
Cryptocurrency Money Laundering
Since its inception, cryptocurrency has been used to launder money. Virtually being untraceable in many aspects here are a few statistics of Money Laundering through Cryptocurrency.
- 99% of cryptocurrency transactions are regulated through AML-compliant exchanges.
- During 2020, cybercrimes through cryptocurrency fell due to strong regulations and KYC/AML procedures.
- Bitcoin Money Laundering is 0.9% of the total Money Laundering in the US and 0.3% globally.
- Money Laundering through Trading
Due to the complex international laws & regulations in trade and trade barriers, money launderers exploit the situation. The invoices of the value of goods and services can be a tool for this illicit practice worldwide. Hence, due to the limitations in Anti-Money Laundering checks in international trading, the Money Launderers get away with it.
Reselling Assets
Seemingly, cash is legitimate through reselling of assets. Big-price items might be bought and resold at the earliest. So, they go for luxury cars, elite real estate, and other commodities for Money Laundering Placement.
Also Read: Reverse Money Laundering
Final Word
Money laundering is a stage-wise and complex activity to catch. But with the passing years, AML trends in 2023 are getting stronger. Also, the digitization of the KYC AML is supported a lot in this course. Money Launderers are also becoming advanced and introducing new ways to launder money. As every system has loopholes, it is necessary for the authorities to regulate the systems with advanced AML compliance.





