Definition of Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
Anti Money Laundering (AML) is a set of rules, guidelines, and regulations focused on the prevention of Money Laundering and Counterfeiting Terrorism Financing. This approach allows law enforcement to hold money launderers and other criminals accountable before they commit a crime.
Global Impact of Money Laundering
Money Laundering is a universal crime and is growing like cancer. Different ways of injecting illegal funds into the legal financial circle have shaken its foundations. Indeed, Money Laundering has caused serious damage to the global economy. Here are 5 negative impacts of Money Laundering on the economy worldwide:
1) Corruption
Firstly, it is the best hideout for corrupt individuals like PEPs (Politically Exposed Persons) and SIPs (Special Interest Persons). Mostly, bribes and illegal confiscation of properties and assets facilitate corrupt and powerful people. Hence, it weakens the legal system and brings economic instability.
2) Organized Crime
Secondly, organized crimes like drug trafficking, human trafficking, murders, and terrorism are funded through Money Laundering. This causes social unrest, violence, and political instability in the country and hinders economic development.
3) Decreased Foreign Investment
Investors will always refuse to invest in an economy where there is a threat of financial crime. Although Anti Money Laundering laws deter the normalization of Money Laundering the risk is there. Since foreign investment is reduced due to financial crimes, the country’s economy might collapse.
4) Tax Evasion
Similarly, Money Laundering is a shelter for tax evasion. People who refuse to pay taxes confiscate the right to social equality. Poor people who can benefit from government-funded facilities will not receive their rights in case of Money Laundering. Tax Havens hinder social services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
What are the 3 Stages of Money Laundering?
Money Laundering is a complex criminal activity and difficult to identify and combat. However, once the whole process is clear and easy to understand, anyone will be able to sense suspicious activities. So, here’s a descriptive table on 3 stages of money laundering.
| Placement |
|
| Layering |
|
| Integration |
|
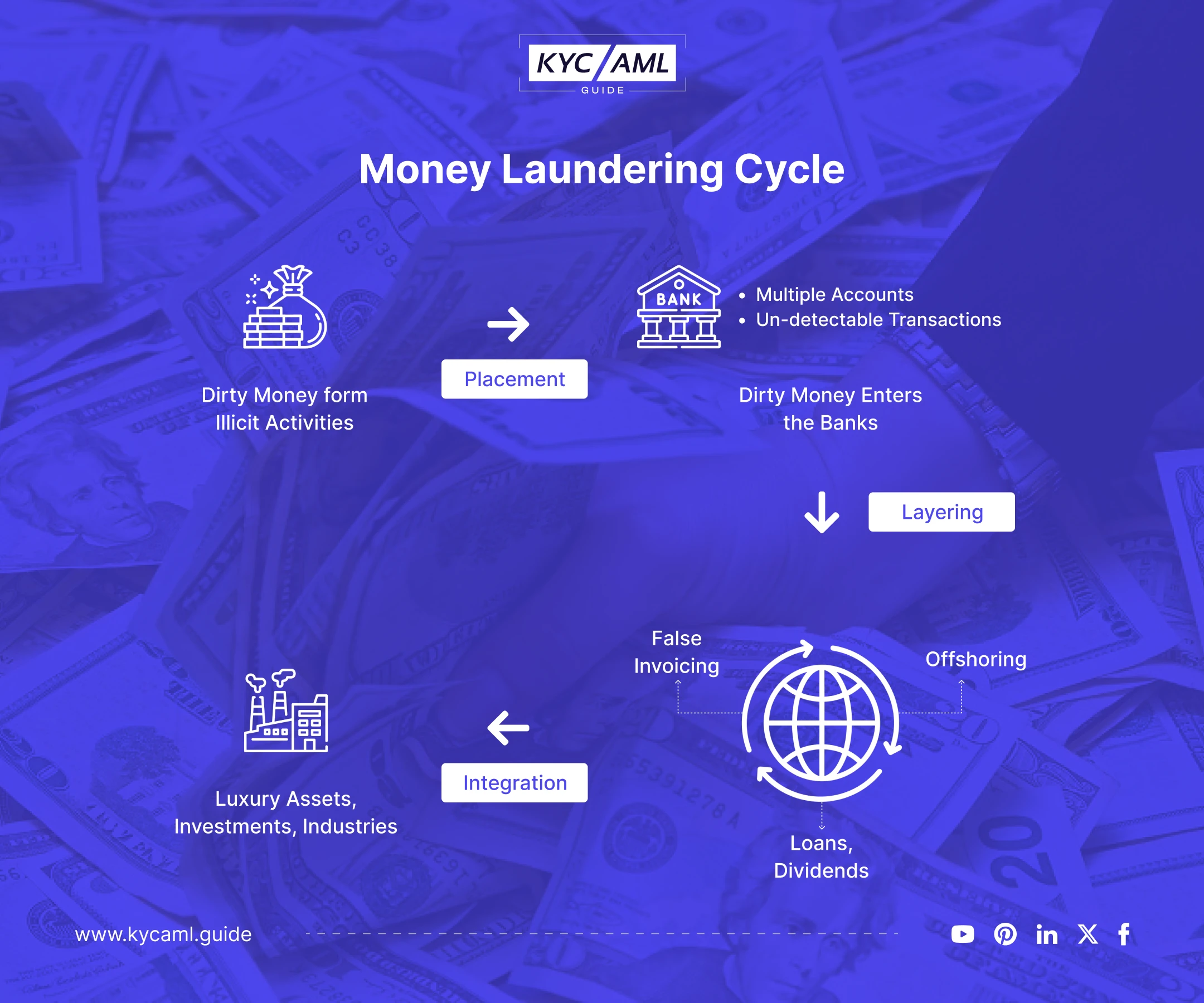
Overall, the Money Laundering stages are the tiers of concealing illegal money. Primarily, the AML compliance team regulates the firms against these layers. So, the firms are better able to understand the
Money Laundering Regulations
Mainly, the following are the AML Regulations in the UK by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). Notably, these regulations are directed by the EU’s 5th Money Laundering Directive included in the AML directives. The standards are set by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
- High-Risk Factors
- E-Money and Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
- Reporting the discrepancies to Company House
- Compliance Under MLRs
- Crypto asset Regulations
Likewise, other authorities support and guide the regulatory framework in Money Laundering Regulations. Here are the main regulatory bodies for AML.
- FinCEN (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network), USA
- FATF (Financial Action Task Force), G7
- FCA (Financial Conduct Authority), UK
- OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control), USA
- PRA (Prudential Regulation Authority), UK
Furthermore, the regulated entities by the AML authorities can be viewed in the linked article above.
Money Laundering checks in Anti Money Laundering
Consequently, the AML checks are carried out to ensure the identification and prevention of Money Laundering at all levels. Possibly, anyone can bypass these checks if the loopholes are exposed in an AML system. Therefore, strong Money Laundering checks are required for KYC Process and Anti Money Laundering compliance.
Red Flags for Money Laundering
Commonly, Red Flag is a term used in Money Laundering that refers to suspicious activity or a warning sign. It suggests a high risk of Money Laundering or other Financial crime is evident in a transaction. So it is a mandatory requirement for banks and financial institutions to file SAR (Suspicious Activity Report). In this case, they are alert to Red Flags, and the SAR is filed to the FinCEN. Similarly, for other countries, the SAR is submitted to the relevant regulatory body.
Red Flags indicators can be:
- High-Risk Transactions, Countries, and Individuals identified through Ongoing Monitoring.
- Unusual and suspicious transaction patterns including large cash deposits and withdrawals.
- Unclear and undeclared sources of funds and beneficial ownership of bank accounts.
- Suspicious behavior like reluctance in proving identity or having multiple accounts.
It can be said that Red Flags are a Risk-Based Approach to prevent Money Laundering. Moreover, the KYC Process includes Customer Due Diligence and Enhanced Due Diligence that support the same cause. Hence, both KYC and AML have the same motive which is to prevent Financial Crime. Additionally, raising Red Flags is the best way to identify Money Laundering and other financial crimes.
AML Compliance
Accordingly, Anti Money Laundering compliance is a measure taken by businesses and FIs to detect and prevent Money Laundering. Particularly, an AML compliance officer has the core duty to ensure KYC and AML regulatory compliance which entails the following key areas:
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
- Transaction Monitoring
- Risk Assessment
- Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR)
- Record-Keeping
- Staff Training
- Compliance Program
AML CFT
While explaining AML compliance, we should also understand the two interconnected concepts of AML and CFT. Below is a compare and contrast point-wise explanation of both concepts
| AML (Anti-Money Laundering) | CFT (Combating Financing of Terrorism) |
| Regulations, Policies, and Procedures for the detection and prevention of Money Laundering. | Measures aimed to detect and prevent Terrorism Financing. |
| AML compliance is internationally regulated. | CFT compliance is regulated by national bodies. |
| AML detects and reports the Money Laundering risk. | CFT detects and reports the terrorist financing risks. |
Both AML and CFT are focused on the firm’s regulatory compliance status. Also, both are requirements for a robust KYC system. Furthermore, AML verification is required for a foolproof and secure financial system in which criminals cannot find a harbor. For this purpose, Identity verification & Authentication are carried out through digital identity management.
AML Audit
AML Audit is the process of reviewing and evaluating the Anti Money Laundering program. Its effectiveness and weaknesses are checked through an AML audit for further improvements. The following points illustrate the AML Audit and its link to KYC/AML compliance.
- The scope of the audit defines the areas where an AML audit needs to be performed.
- Risk Assessment is carried out for the AML risk profile of an organization.
- Compliance with Regulations ensures the AML regulations are strictly adhered to by the USA Patriot Act and BSA (Bank Secrecy Act)
- Policies and Procedures need to be communicated to all relevant parties
- Customer Due Diligence, Transaction Monitoring, Training, and Reporting activities should also be included in AML programs.
- The AML Auditor shall carry out regular follow-ups for ongoing improvements in the system.
The video explains that the most suitable person to conduct the AML Audit should not be an internal employee including an MLRO, a compliance team member, or a person from the department that has a conflict of interest like someone from sales. After the neutral and most suited Audit candidate is selected, the scope and extent of the audit should be documented to cover the above-mentioned points in the audit.
How KYC AML Guide helps you to prevent Money Laundering
Businesses strive to stay compliant and avoid hefty fines and penalties in case the Identity Verification solution has vulnerabilities concerning customer identities. Suspicious customers if onboarded can lead to misuse of services through identity theft or fake IDs for money laundering and other illicit financial activities. Hence, the businesses can undergo a hectic and protracted legal procedure. To prevent this, expert guidance in selecting the right KYC and AML Solution provider is mandatory which itself can drain significant resources.
KYC AML Guide resolves this problem by helping you through our KYC Technology Buying Consultancy supplemented by our meticulous Vendor Analysis. We are experts in steering clients in the right direction to ensure cost savings, guaranteed results in foolproof Identity Verification, and the best-suited solution for your requirements.
Conclusion
Anti-money laundering is important for firms and everyone involved in businesses with a high volume of transactions. However, it does not mean that AML regulations do not apply to non-financial businesses. So far, almost every business that is listed as a legal entity type is somehow regulated under the AML laws of the relevant jurisdiction. However, there are non-regulated jurisdictions that are a big concern for global regulatory authorities.
Globally, AML compliance is carried out through updated AML solutions. It is also recommended that strong AML compliance requires comprehensive knowledge of the industry and regulatory requirements. Fintech firms and other businesses must focus on the importance of a digitized and effective KYC/AML solution for enhanced compliance and security. Making the financial sector safe and secure for everyone is the responsibility of everyone connected to it.





