What is Integration Stage in Money Laundering?
Integration is the third and final stage in the Money Laundering process in which Money is considered to be cleaned and enters the legal financial circle. After this stage, it is nearly impossible for law enforcement and regulatory agencies to identify or trace the money trails back to the owner. Thus, money that enters the legal system after integration appears legal.
There are 2 main objectives of Integration:
- Removing the Suspicion
- Effective and Undetectable Layering
As money enters this stage after a complex layering stage, it’s easy to utilize it in purchasing legal goods and services or investing it legally. Layering involves a complex web of purchases, investments, and cover-up transactions (shell companies, etc.) so it is easy to wipe out the final suspicion in integration.
Main Businesses that help carry out Integration
Mainly, the Integration stage requires the money launderer to have a strong network in the legitimate business circle. Criminals maintain a high-profile social circle and connection with industrial tycoons worldwide.
Here are a few legitimate businesses that facilitate Money Laundering in the integration stage.
| Real Estate | Money Launderers invest in real estate with layered cash and obtain legal documentation from real estate firms. If by any chance, the law enforcement questions the purchase or the origin of money, the investors (money launderers) show them the legal documentation of real estate purchases.
Read More about Money Laundering Risk in Real Estate |
| Trade-Based Money Laundering (TBML) | The movement of cash in cross-border transactions through international trade. Cash is not physically moved rather the criminals use legitimate international trade transactions as a disguise to launder their illicit money.
Read More about TBML |
| High-Value Assets | Criminals enjoy a luxurious lifestyle with laundered money. They make purchases of high-value goods in auctions and bid the highest price |
| Cryptocurrencies | Cryptocurrencies are a popular and fast-growing source to carry out transactions internationally and locally. Due to high speed and high anonymity levels, it is difficult to regulate them and detect money laundering activity in digital assets. However, FATF’s Crypto Travel Rule and other regulations are initiatives taken by |
| Other Businesses | Other legal businesses that are used for Money Laundering Integration are:
Legal businesses provide legal documentation to the beneficiaries and investors. |
How to Identify Integration Stage in Money Laundering?
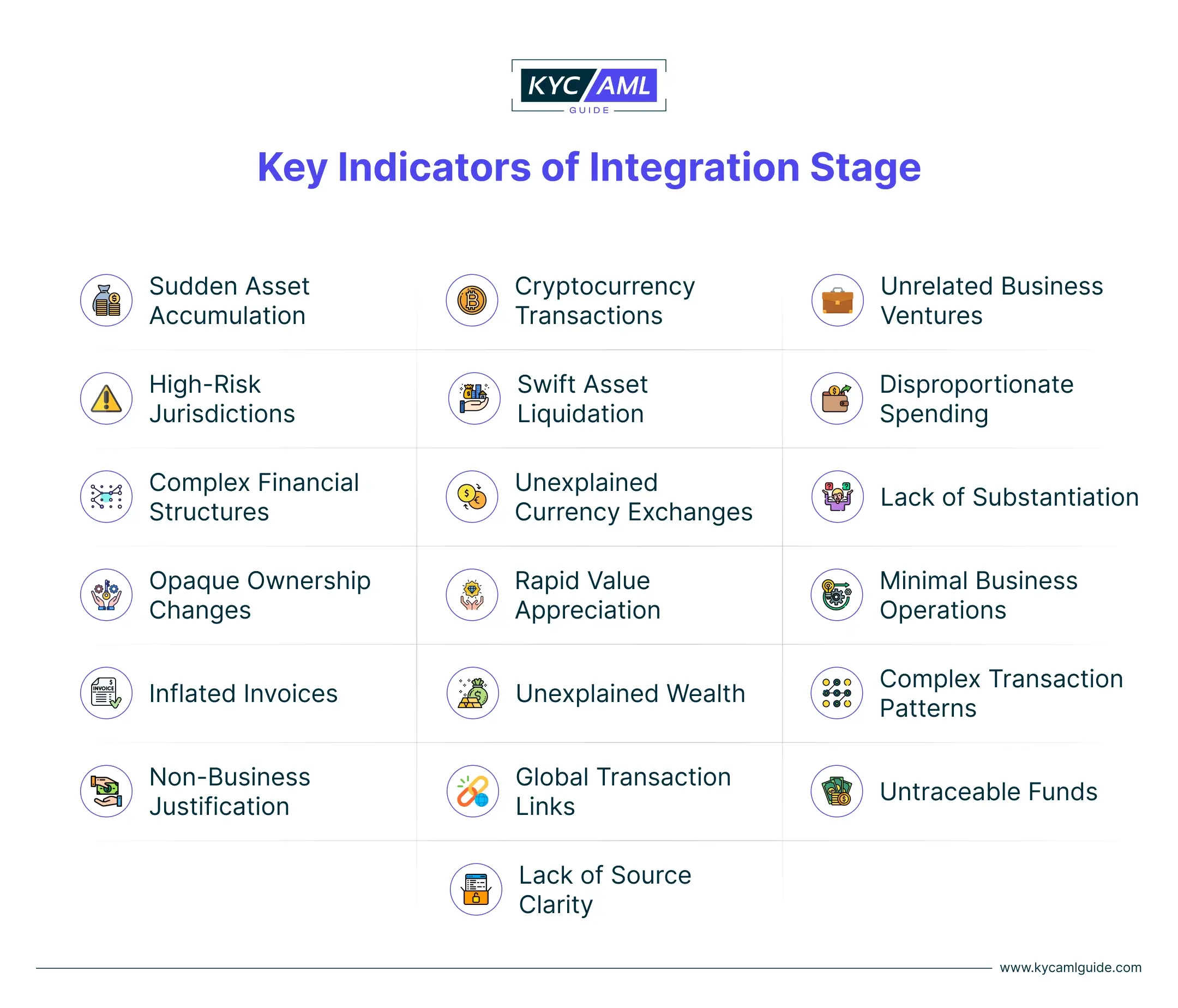
Identifying the Integration of Money for hiding illegal cash is complicated. Yet, through the implementation of digital KYC (eKYC), Ongoing Monitoring of Transactions, and staying updated with regulatory compliance framework, Authorities, and Firms can enhance their ability to detect Integration attempts. View the graphical illustration below to know the Key signs of potential Integration activity.
How Does a KYC AML System Help in Stopping Integration?
Mitigation of money laundering risk is one of the core responsibilities of any KYC and AML system. An effective KYC/AML system not only detects and reports money laundering activity but prevents illicit funds from entering the system. Following are the features of a KYC/AML System that help in the prevention of Integration Money Laundering:
| 1 | Identity Verification | KYC and AML system allows genuine customer onboarding and minimizes the chances of fake and fraudulent identities that are used for money laundering. |
| 2 | Validity of Sources of Fund | KYC and AML regulations have a requirement of a certain level of transparency in disclosing funds sources to stop illicit money from entering the legal financial system. |
| 3 | Transaction Monitoring | AML and KYC system detects complex and unusual transactions that indicate integration patterns and attempts to conceal illicit money. |
| 4 | Risk Categorization | Defining PEP Levels and identifying UBOs and other risk factors is one of the core elements in a KYC/AML compliance system. It subjects higher risk profiles to a stringent screening process.
Read Also: PEP Screening | KYC AML Guide |
| 5 | Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) | The in-depth due diligence process in AML (Anti-Money Laundering) triggers comprehensive verification for high-risk clients and prevents integration. |
| 6 | Geographic Risks | High-risk countries due to sanctions, war, and terrorist activities are usually flagged. KYC and AML systems integrate different technologies to maintain updated databases of risky geo-locations. |
| 7 | Customer Behavior | AML and KYC use customers’ previous behavior patterns compares them with existing behavior and finds mismatches or suspicious activities to identify money laundering and other financial crime. |
| 8 | Transaction Limits | AML curbs rapid fund movement, impeding integration speed. |
| 9 | Traces of Funds | Funds are traced systematically and at a high pace in a digital KYC and AML system. This helps in keeping a watchful eye on the money trail and linking it back to the origin. |
| 10 | Secure Data Sharing | Valuable information and data are shared securely through a KYC and AML system. |
| 11 | Compliance Training | Training is an essential part of KYC AML System implementation throughout the organization. Employees as well as management must embrace the importance of compliance and stay updated through training. |
| 12 | Regulatory Adherence | KYC and AML system ensures regulatory compliance adherence and discourages Financial institutions from aiding Integration and other stages of Money laundering. |
| 13 | Ongoing Monitoring | Ongoing Monitoring helps in spotting sudden changes and raising red flags if needed in the entire financial ecosystem. |
| 14 | Reporting Suspicious Activity | Suspicious Activity Reporting prevents any possible money laundering risk. |
| 15 | Supporting Enforcement Actions | A robust KYC and AML system facilitates enforcement actions by providing strong evidence against the money launderers. |
Final Words
Integration serves as the ultimate camouflage in the intricate web of Money Laundering, covering the tracks of criminals by hiding their illegally earned money. The World Economic Forum has estimated that Money Laundering accounts for 2 to 5% of global GDP totaling from $1.4 to $3.5 trillion annually. As money launderers are advancing with the use of technology, it is digital KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) that stand between financial integrity and criminals penetrating the legal financial ecosystem. These digital guardians actively verify identities, trace fund origins and monitor transactions to prevent integration attempts.
It is vitally important that a globally coordinated and collaborative effort is required in order to streamline the implementation of KYC and AML regulations at every possible level.





