What is Digital Identity?
A digital identity is information about a living person that is available digitally online. This information is used for different purposes such as signing up for different services. It is different from the physical identity of a person for example a driving license or an ID card. Digital Identity includes information like location, website surfing analytics, and digital account details. Also, it can include information like scanned copies of physical documents.
OECD recommends the implementation of Digital Identities in the EU’s government system with three pillars:
- Developing a user-centered and inclusive digital identity system
- Strengthening the governance of digital identity
- Enabling cross-border use of digital identity
OECD adherents state that:
“As society is digitalizing every day, the need for effective digital identity solutions has become increasingly important. However, a single system will not suffice as these solutions are highly contextual and must be integrated into a larger ecosystem that addresses the challenges with entirety.”
Importance of DIMS in KYC and AML
eKYC and eIDV are the two advanced approaches in Customer Identification and Onboarding. Both of them are directly related to the use of digital identity in KYC and AML procedures. Since digital identity verification is required for the Know Your Customer and Anti-Money Laundering process nowadays, digital identity has not only benefited the customers but also made the system more secure.
To uncover the challenges faced in Identity Verification and steering Onboarding Professionals through the best KYC Practices to cover a wide range of user-profiles and personas, read the KYC AML Guide’s whitepaper on Challenges in KYC Identity Verification.
Challenges in Digital Identity Management
Digital Identities are helpful yet challenging in identifying criminals. Some major challenges faced in digitizing Identity Management are:
- Security Concern: Since online information can be hacked easily, the security of digital identity is compromised if not protected well. Cybercriminals are always stalking for loosely covered digital identities where they can hack and misuse the digital identity for money laundering, and other crimes.
- Privacy Concern: Users’ privacy is compromised to the extent that their private details can be used to threaten them with extortion as well.
- Login Mechanism Issue: Sometimes digital identity can be a problem as the complexities of the login mechanisms such as strong and difficult passwords, retina, and fingerprint scanning can be a nuisance to the users.
- Monitoring: Digital Identity Management also requires ongoing monitoring to keep it fair and equitable for everyone connected.
The Role of Blockchain in Enhancing DIMS
In recent years, Blockchain technology warehousing, transparency, traceability, and tamper-resistance. Through its secure and systematic data and other attributes, it has become the need of the time for streamlining Identity Verification in businesses. Almost every business that requires database management, is using blockchain somehow. Many industry experts recommend fast implementation of blockchain technology in Digital IDM to stay ahead of criminals.
Also Read: Exploring NFC Identity Verification | KYC AML Guide
Three Architectures of Blockchain-based Digital IDMVS
Identity Management is a complex and step-wise process. Basically, there are three architectural approaches to implementing blockchain technology for Digital Identity Management.
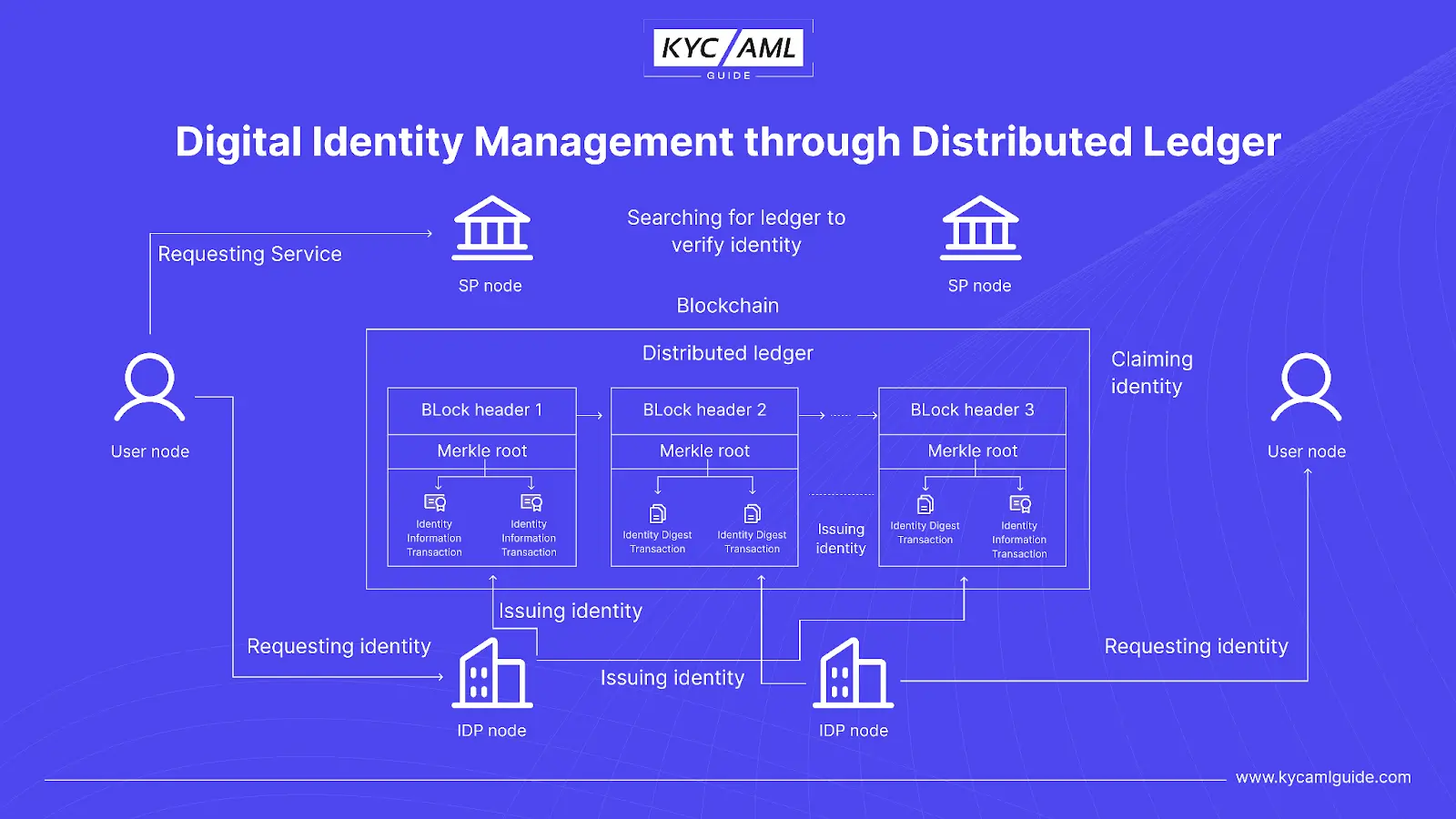
Distributed Ledger
This architecture ensures that there is no issuance of malicious certificates. Digital Identities are stored in a database maintained on the hash digests. It enables the cross-domain verification and traceability of issued certificates.
Smart Contract
In this architecture, smart contracts of the blockchain are used for authorization of digital identity and their claim.
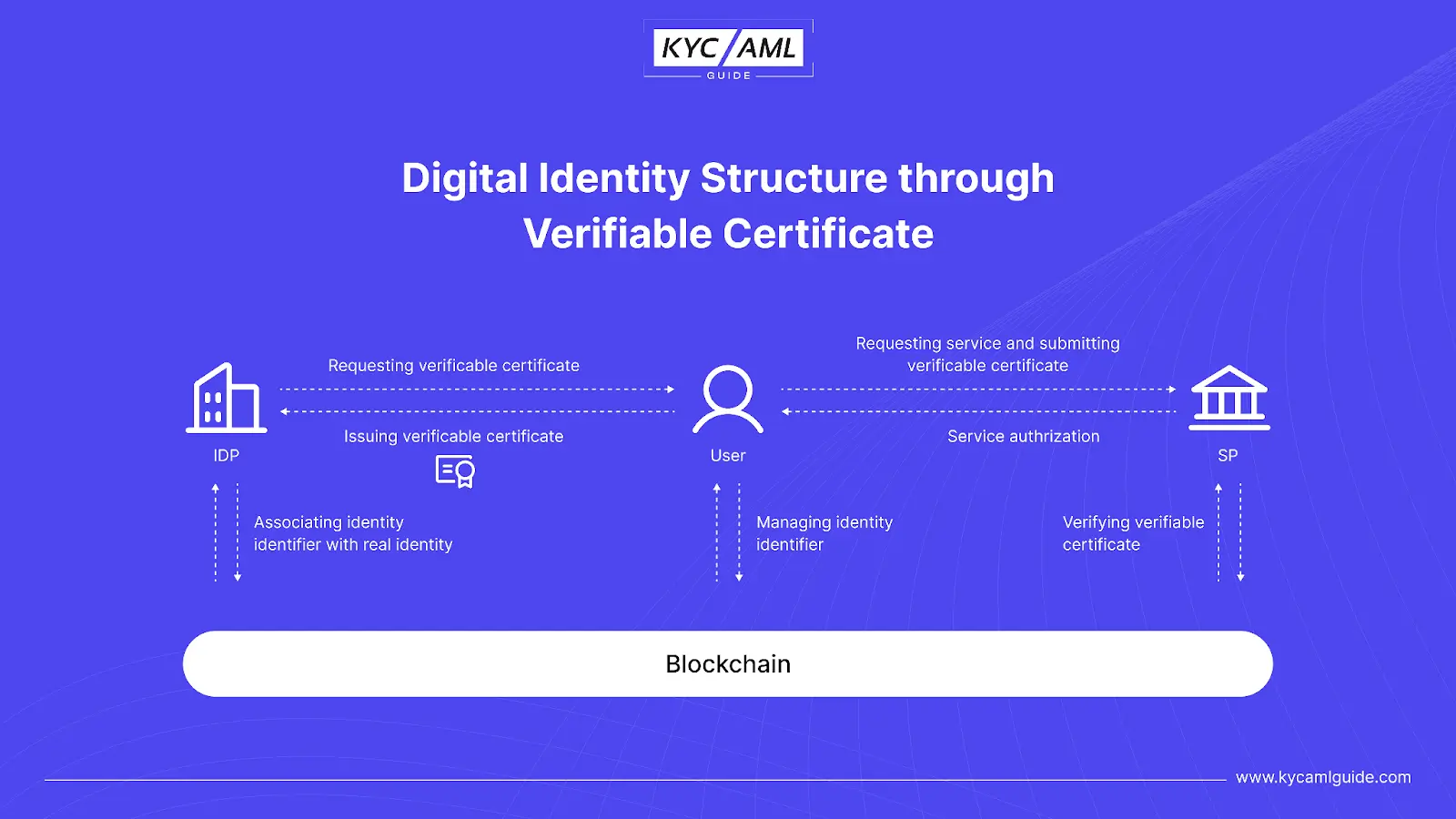
Verifiable Certificate
A verifiable Certificate is a comparatively simpler architecture of blockchain in Digital Identity Management. While the verifiable certificate (VC) is being used for digital identity, blockchain is not publicly available to store or publish digital identity. Mainly, it is focused on integrating real identity with digital identity through identifiers.
Advantages of Blockchain-based Digital IDM
| Increased Security | In Digital Identity Verification, the use of blockchain technology was primarily introduced for increased security. Since its implementation, the databases of digital identities have become secure. As the personal details in digital identity can be used for fraud, and scams through identity theft, Blockchain minimizes this threat through architectural schemes. |
| Greater Transparency | Users and customers can now easily access their own digital identities in a blockchain which enables a higher level of transparency. |
| Decentralization | Blockchain technology is preferred due to its decentralized nature, the accessibility, monitoring, and management of the architecture are easier for digital identities. |
| Increased Efficiency | Digital Identity Management requires a high level of efficiency when it is dealing with billions of records. Blockchain being a highly efficient system enables efficient database management. |
| Lower Costs | No third party is required for the deployment and maintenance of the digital identity platform in a blockchain, the cost is reduced. |
Ethical Considerations in Digital Identities
We must embrace the bitter truth that any system can have loopholes in it. It can also have walkthroughs from where fraudsters and criminals can penetrate. In simple words, honesty is the best policy where ethical training of employees, customers, and everyone associated is mandatory. Otherwise, anyone can misuse the system and commit a crime. Following are the three main areas where Ethical considerations lie in digital identity.
Ethical Model for Digital Identity Management
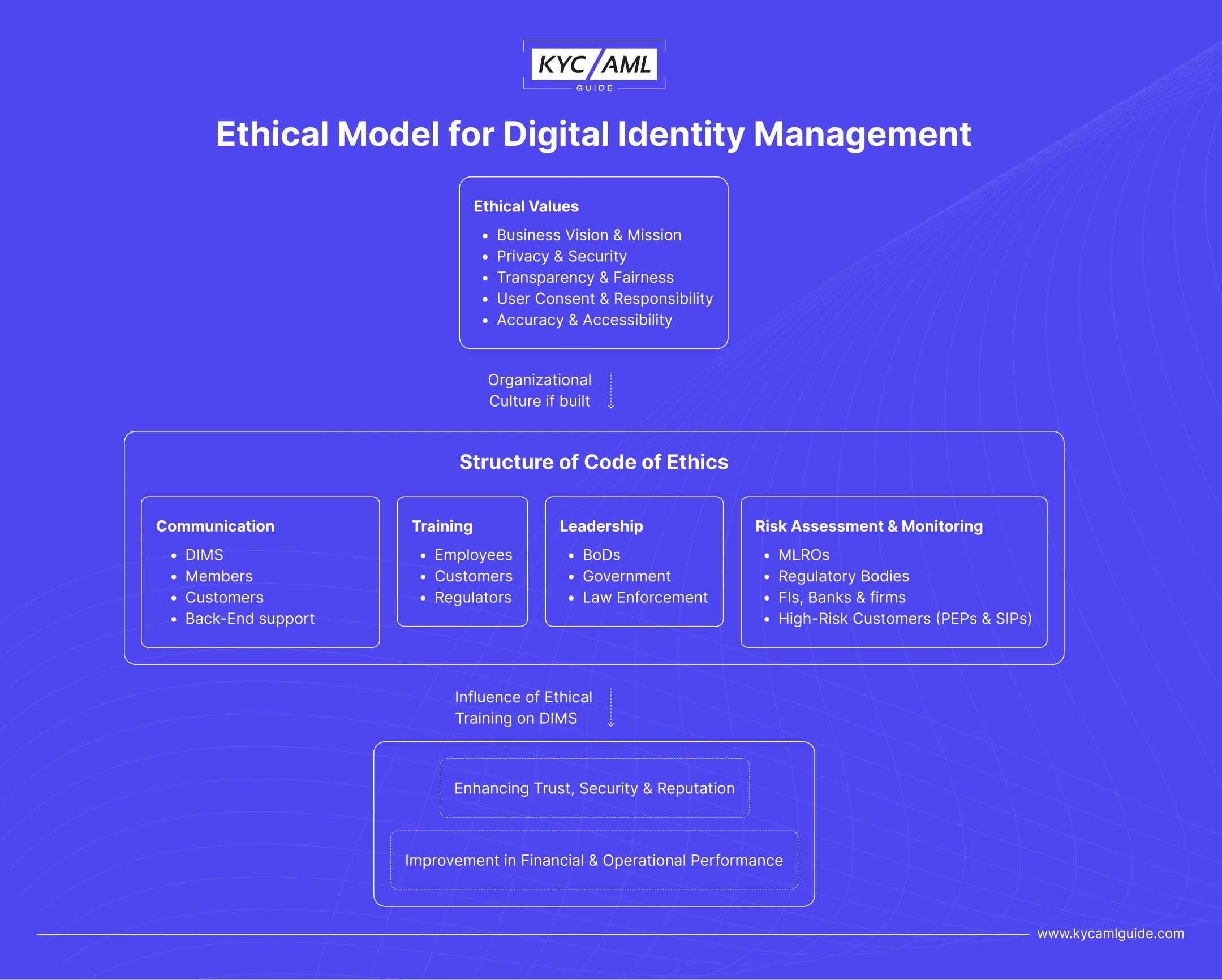
8 Elements of Ethical Training in Digital Identity Management
| 1 | Privacy | Personal information is highly sensitive and needs to be protected from unauthorized access. It is the user’s right to privacy that his or her information must be kept private and not disclosed publicly. Digital Identity systems must be strict on privacy policies to ensure personal data is collected and used only for the intended purpose. |
| 2 | Security | Digital Identity systems must be secure for the prevention of data breaches and unauthorized access. Security measures should be updated and fool-proof to ensure that the data is fully protected and secure from hackers and other criminals. |
| 3 | Consent | Users should be aware of what data is being collected, and how it is being used, and have given their consent to the collection and use of their personal data. |
| 4 | Transparency | DIMS should be transparent about its data collection, storage, and usage to ensure insider security of data from any misuse. |
| 5 | Fairness | It should treat all users fairly and avoid discrimination or bias based on any social element such as gender, race, religious background, or ethnicity. |
| 6 | Accuracy | It must ensure that personal information is accurate and up-to-date. The database should be regularly updated |
| 7 | Accessibility | Digital Identity Management System should be accessible to all users, regardless of their disabilities. However, the level of access may differ to protect the user information and the firm’s reputation. |
| 8 | Responsibility | DIM providers should take responsibility for the user’s data, its security, and its use for only intended purposes. |
News Update: Industry Coalition’s Plea To White House For Enhanced Digital Identities
The Potential for Money Laundering and Fraud
By implementing Digital Identity Solutions in KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering), the risk of money laundering & fraud is greatly reduced. Since the compliance industry relies on the safety and security of customers’ data, the DIMS provides blockchain-based secure Identity solutions. Also, the system’s security protocols & mechanisms are regularly updated for combating the upgraded money laundering and fraud schemes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Blockchain-based Digital Identity Management is a way of the future for identity proofing. The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain technology has benefitted customers in terms of security, privacy, and efficiency. The need for intermediaries is eliminated and DIMS through blockchain allows individuals to have greater control over their personal information. Furthermore, the information cannot be tampered with or manipulated by criminals.
Lastly, with the rise of digital transactions and online interactions, the need for Digital Identity Solutions has increased. Potentially transforming various industries, such as finance, healthcare, and government, Blockchain-based DIMS is assured to revolutionize the way we think about identity verification and authentication in the years to come.
Explore more about Effective Identity Verification through 4 Pillars of KYC





