The KYC process is a significant part of the Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance process. Even though KYC is for the customer, the extension is focused on business and is called Know Your Business (KYB). Like e-KYC, e-KYB is done digitally. As customer and business data can be submitted, researched, and reviewed online, the e-KYB and e-KYC process is turning out to be progressively far-reaching because of regulatory requirements imposed by various jurisdictions globally. As a business owner or a customer, one should be familiar with the e-KYB & e-KYC process.
What is e-KYC?
Electronic KYC (e-KYC) is the process of verifying identity digitally and other KYC necessities. These can take various forms relying upon the business, business needs, use cases, and even customers, yet it usually includes electronic structures, digital documents, and varying levels of automation. Like traditional KYC, e-KYC is normally done during account setup and afterward over the long haul. With the transition to e-KYC, a few nations, like India and Estonia, have additionally begun issuing electronic forms of identification (eIDs) that serve the same purpose as physical documents.
The worldwide e-KYC market size will reach US $673.2 M by 2023. Looking forward, IMARC Group anticipates that the market should reach US $3,398.5 M by 2032, at a CAGR of 19.71%. e-KYC can provide organizations with a complete image of who their clients are. While traditional KYC depends on active and third-party signals, e-KYC joins this information with passive and behavioral signals that are challenging to gauge during the manual process. The different forms of signals required for effective e-KYC implementation are given below.

e-KYC Process Explained
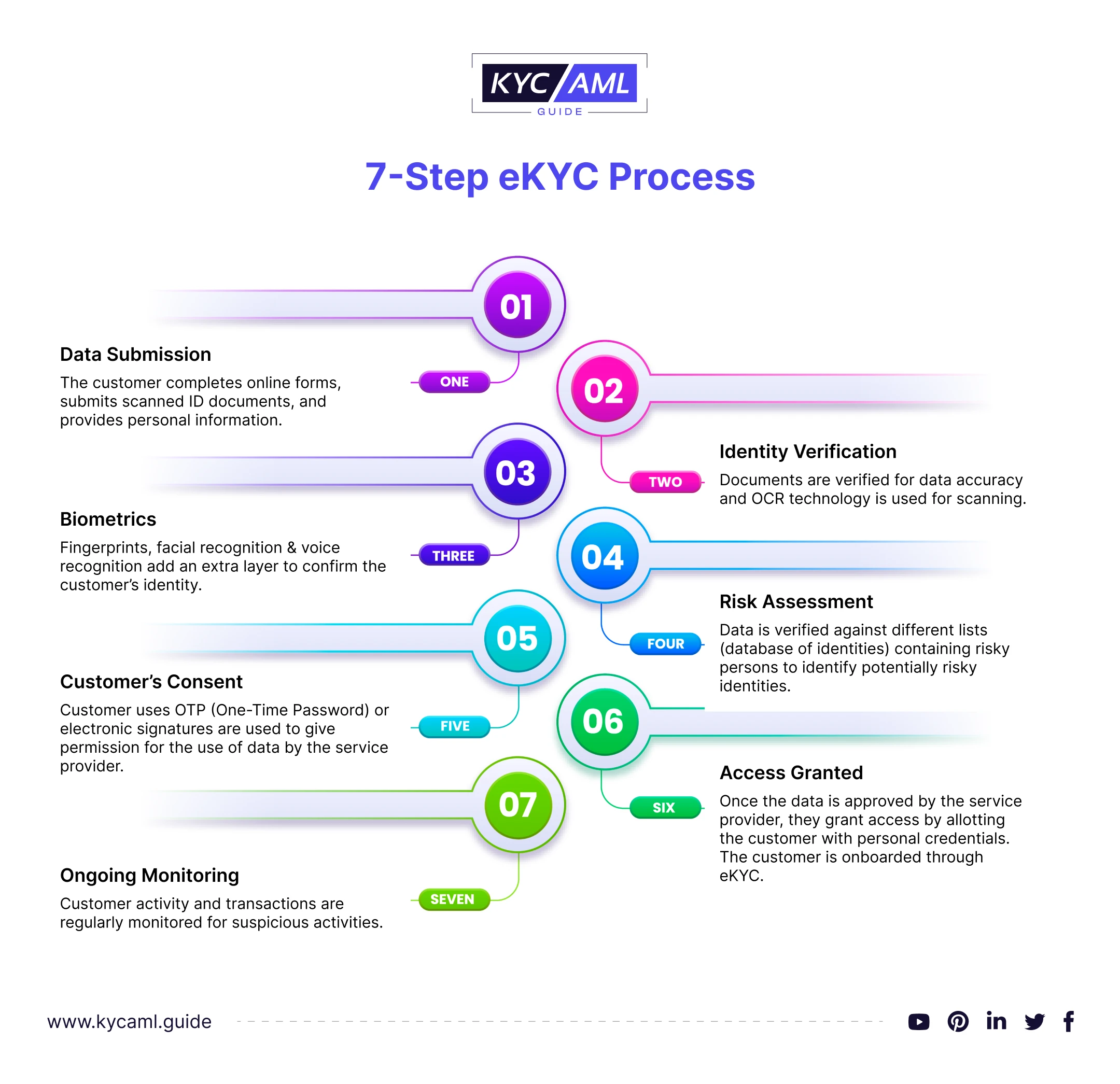
1 Data Submission
Customers complete an online form, submit scanned copies of identification documents, and provide other required information such as personal data and identity documents (Government-issued ID card, bank statement, etc.).
2 Identity Verification
For document verification, OCR technology is used to determine the accuracy of the documents.
3 Biometrics
To enhance the authenticity biometric verification techniques such as fingerprints, facial recognition & voice recognition are used to verify the customer’s identity..
4 Risk Assessment
To identify potentially high-risk identities, data is checked against multiple database lists such as the PEP list, sanction list, AML watchlist, and Global watchlist containing high-risk individuals.
5 Customer’s Consent
Customers authorize the service provider to use their data using an OTP (one-time password) or an electronic signature.
6 Access Granted
The customer is onboarded via e-KYC and is granted access to the services by providing personal credentials once the data has been approved by the service provider.
7 Ongoing Monitoring
Ongoing monitoring is carried out for customer activity and transactions by monitoring suspicious activities.
What is e-KYB?
e-KYB represents Electronic Know Your Business. e-KYB process helps accelerate business-to-business deals and close them on time. KYB regulations are essential for the Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorism (CFT) regimes introduced to reduce unlawful funding.
KYC alone was not enough to address the complexities of B2B relationships, where companies can be used as a safeguard against money laundering. KYB is a new requirement as authorities recognize that companies can be used as a vehicles to transfer illegal money. KYB is an extension of KYC but focuses on businesses. This includes verifying the business, understanding its ownership and the nature of its business operations, and assessing its risk of financial loss. Therefore, before doing business with other companies, you must comply with KYB regulations to protect your interests. You need to know whether corrupt shareholders or businesspeople are using your revenue for illegal purposes by lifting the corporate veil.
e-KYB Process Explained
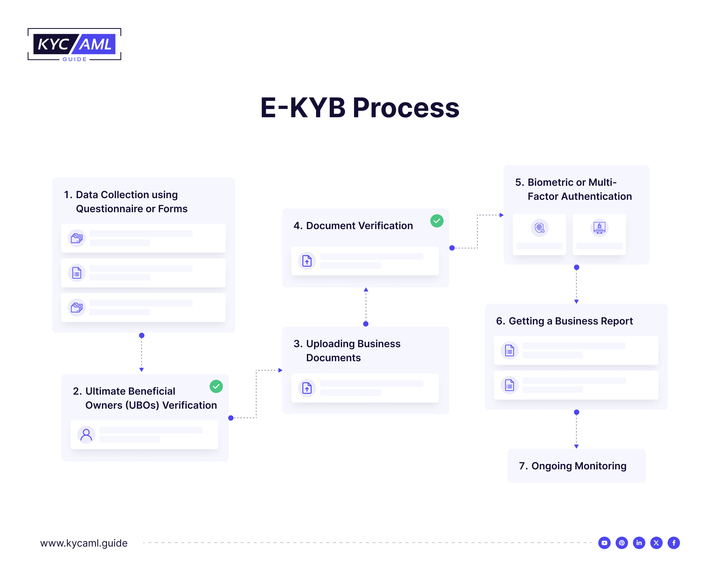
The e-KYB process checks whether the organizations you work with are real companies or shell companies. A significant part of the e-KYB process is to identify the ultimate beneficial owner (UBO) of the company. The following are the steps involved in the e-KYB process.
1 Data Collection
To determine the level of business authenticity, an online questionnaire or form is used to collect business information. Company data collection may include checking the following documents:
- Business name
- Business registration number
- Business country residence
- Business website
- Business register location
- Business postal address
- Business shareholders
- Business UBOs
2 Ultimate Beneficial Owners (UBOs) Verification
Beneficiaries, shareholders, and authorized representatives of the company must undergo e-KYC verification. The KYC verification of UBOs, shareholders, and authorized representatives aims to ensure that they are not politically exposed persons (PEPs) or blacklisted persons.
3 Uploading Business Documents
Companies must upload legal documents online to support their claims for verification purposes. These documents contain all the necessary KYB documents that support the legal existence of the company. The submission of the documents depends on the type and jurisdiction of the business. The documents are
- Articles of Incorporation and Association
- Certificate of Incorporation
- Copy of Shareholder registry
- Memorandum
- Copy of State Business Registry
- Copy of Director registry, etc.
4 Document Verification
To ensure authenticity and accuracy submitted documents are digitally verified. This may include advanced technologies such as optical character recognition (OCR) for text extraction.
5 Biometric or Multi-Factor Authentication
Some eKYB processes may include a biometric or multi-factor authentication process to verify the identity of key parties involved in the business for security purposes.
6 Getting a Business Report
After completing all the steps, the applicant can download the company report after verification from the KYB Solutions company.
7 Ongoing Monitoring
Once you are convinced that the company and key people are a good fit to work with, it is important to do more research. Just like e-KYC, e-KYB is not something you need to do just during onboarding. The CDD final rule requires covered entities to “investigate and report suspicious transactions and maintain and update customer data based on risk”.
This way you can verify the identity of the company and the beneficial owner of the company. You can determine whether the company’s risk profile matches the intended business relationship.
Benefits of e-KYB & e-KYC process.
Better Efficiency:
The e-KYB & e-KYC process can handle a large number of KYC/KYB checks in a short period, streamlining the onboarding process and the time required to resolve issues.
Improved Accuracy:
The e-KYB & e-KYC process reduces the risk of human error. Companies can ensure consistent and reliable results by using automated algorithms on existing data. It leads to more accurate decisions and reduces the chance of data entry errors or mistakes in the KYC remediation process.
Scalability:
The manual KYC and KYB verification process can be time-consuming and tedious, especially during high demand or when dealing with multiple customer requests. The e-KYB & e-KYC processes offer scalability, enabling companies to scale projects without sacrificing efficiency or accuracy, thereby maintaining an efficient and consistent screening process.
Risk Mitigation:
The e-KYB & e-KYC process is a critical risk indicator for companies focused on mitigating risks associated with onboarding or during enhanced due diligence (EDD). These features help identify potential risks and prevent unauthorized access to the financial system.
For the end user, the benefits of the e-KYB & e-KYC process include:
- Individuals and businesses can fill out forms and applications without scanning physical documents, printing physical forms, or visiting physical departments or offices.
- Customers get faster support and account creation because electronic data can be automatically verified.
- When companies adopt eKYC, it means fewer people check sensitive data because the system does it automatically. This means that customers generally experience greater privacy.
How Can Companies Implement e-KYB & e-KYC process?
For businesses looking to upgrade from manual to e-KYB & e-KYC process, one of the first things to consider is which technology or combination of technologies will work. It is important to measure customer requirements and compliance requirements, information security, ease of installation for customers, and available budget. KYC AML guide can provide you with research-based consultancy to choose the best solution for your digital KYC & KYB requirements.





