Overview of eKYC
The ability to digitize the customer onboarding process includes the KYC. Mostly, it is considered a vitally important activity in the Business & finance sector. However, electronic KYC is an advancement to the traditional KYC process. It leverages Artificial Intelligence alongside many other emerging technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), Biometrics, Facial Recognition, and Live checks, which are embedded with Machine Learning to digitize manual KYC. So, it makes the KYC process paperless, seamless, and effortless.
Also, Read NFC Identity Verification | KYC AML Guide
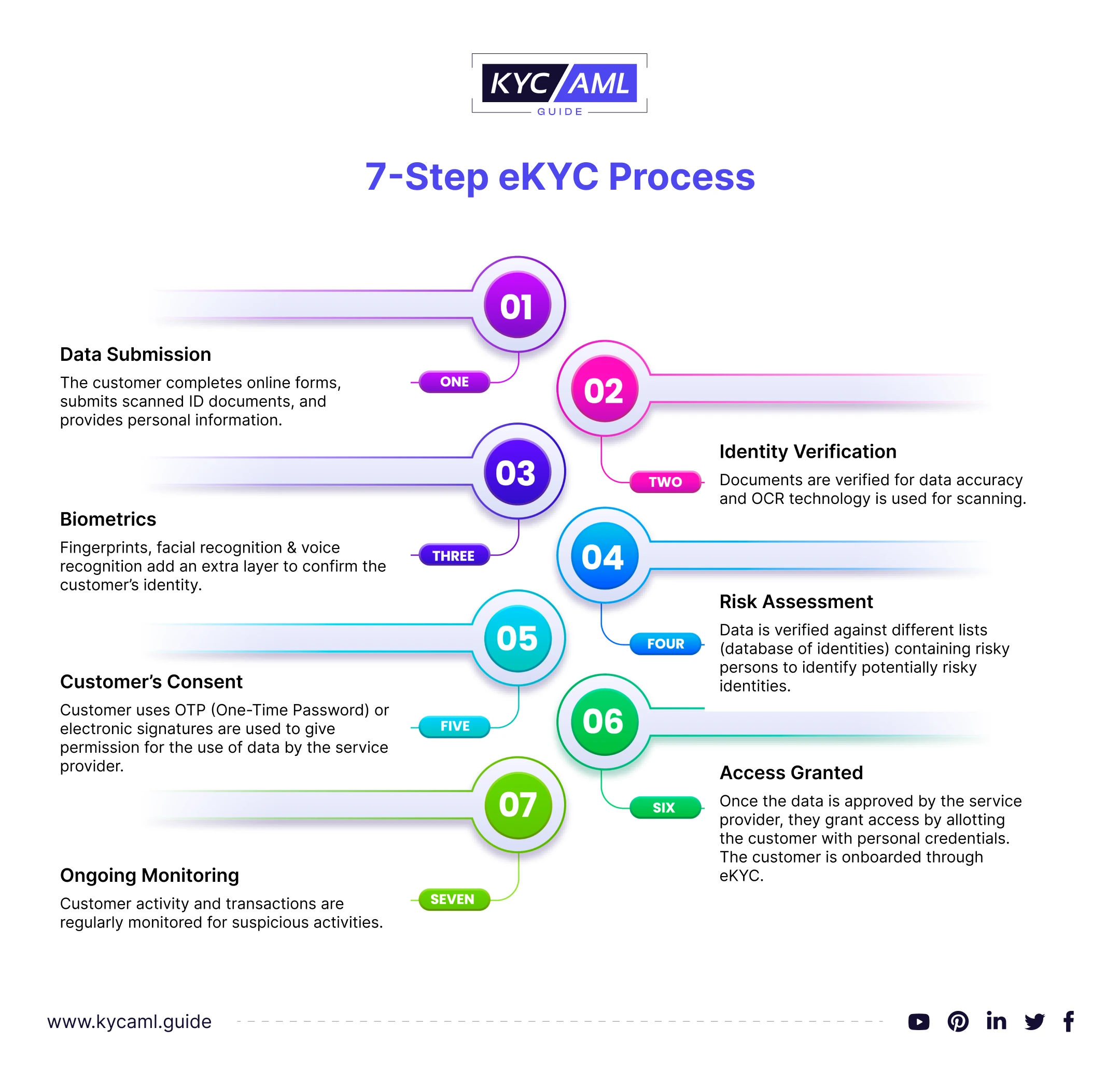
eKYC Process Explained
| 1 | Data Submission | The customer fills out online forms, submits scanned copies of Identifiable documents & provides other necessary information. It includes personal details and other Identity documents. |
| 2 | Identity Verification | Documents are verified for data accuracy and OCR technology is used for scanning. |
| 3 | Biometrics | Fingerprints, facial recognition & voice recognition add an extra layer to confirm the customer’s identity. |
| 4 | Risk Assessment | Data is verified against different lists (database of identities) containing risky persons to identify potentially risky identities. |
| 5 | Customer’s Consent | The Customer uses OTP (One-Time Password) or electronic signatures to permit the use of data by the service provider. |
| 6 | Access Granted | Once the data is approved by the service provider, they grant access by allotting the customer with personal credentials. The customer is onboarded through eKYC. |
| 7 | Ongoing Monitoring | Customer activity and transactions are regularly monitored for suspicious activities. |
The link between eKYC and Digital Identity
A Digital Identity is what defines a person, an entity of anyone’s existence online. Unique identifiers and user patterns help detect and identify individuals from their devices. Website owners use the collected information from the devices to track the patterns of use and target them in a personalized way through targeted content. Originally, digital identity was the means to enable eKYC. A digital identity is formed naturally through personal information and online actions. It can be a pseudonym linked to an IP address or a unique ID. Additionally, digital identities are considered contextual as users only provide selective information for authentication.
Difference Between Manual KYC and eKYC
The evolution of Transitional or Manual KYC to eKYC has increased in recent years. Especially, after the COVID-19 pandemic eKYC has taken over most of the KYC globally. There are 11 major differences between manual KYC and Digital KYC. See the table below:
| Aspect | Manual KYC | eKYC |
| Process | It is a manual process with is paper-based. | It is an automated process facilitating customers. |
| Customer’s Presence | The physical presence of the customer (in-person verification) is necessary. | Does not require the physical presence of the customer. It is mostly done remotely through smartphones. |
| Document Submission | Hard-copy documents like utility bills, photocopies of ID documents, etc. | Scanned copies of ID documents are uploaded saving paper cost & time. |
| Processing Time | is Visibly slow due to manual verification. | Fast-paced due to process automation. |
| Accuracy | Low level of accuracy due to human error & inconsistencies. | High level of accuracy through Digital Verification. |
| Customer Experience | Prolonged onboarding due to paperwork. | Digital onboarding offers convenience to enhance customer experience. |
| Cost | High operational cost for document handling and workforce involved. | Low cost due to digitization & lesser workforce. |
| Scalability | Manual processes limit the scalability of Manual KYC. | Highly scalable and can handle larger data volumes. |
| Data Security | Risk of Data theft, and data loss due to physical document mishandling. | Enhanced data security through encryption & data protection through credentials. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Requires adherence and updation to meet KYC/AML regulatory standards. | Improves regulatory compliance through automation in updation. |
| Environmental Impact | Since it is paper-based it is less eco-friendly. | More environmentally stable due to being paperless. |
The above table clarifies and advocates the implementation of Digital KYC to meet the latest onboarding requirements. It is undeniably beneficial and improves overall regulatory compliance. Moreover, an Ideal eKYC solution has these 11 features where different KYC solution providers now focus on digitizing onboarding processes.
Who requires the eKYC?
Primarily, Banks, Financial institutions & other service providers require the eKYC. Other businesses may include:
- Fintech start-ups
- Brokerage firms
- Foreign Exchange
- Insurance Companies
- Crypto Exchanges
- Government Sector
What is required during the Electronic KYC?
Essentially, the data points are required for a digital identity in the electronic KYC process for banks. These include:
- Username/ Password
- Transaction history
- DOB (Date of Birth)
- SSN (USA and other)
- Electronic transactions
- Loan history
Digital Transformation through eKYC
In our earlier publications, we have discussed the regulations of KYC and AML. In the case of banks, we now witness that almost everything is digitalized on the back end. The rapid digitalization led the bank’s operations to require a seamless transition in conducting KYC. Electronic KYC has facilitated the KYC for banking and contributed to the fast-paced banking. More importantly, AI and Machine learning have automated many key processes in KYC. Thus, the eKYC has opened up ways towards new and improved identification & verification processes for banks. Customers, Businesses, and beneficiaries can now do their KYC for bank accounts seamlessly. Also, it helps reduce the time consumed in the CDD process.
Tools in Digital KYC

KYC technology buying itself is a complicated task where clients require knowledgeable guidance to make the right decisions. KYC Vendors have adjusted their services specifically according to their client’s needs but sometimes, a mismatch in requirements and services set can lead to huge losses or failure in compliance. So, to avoid this KYC Technology Buying Consultancy can help save considerable time and cost.
Drawbacks of eKYC in Banking
First, educating the users and customers about electronic KYC is a prevalent problem. The complex methods of opening up bank accounts now irritate many individuals. Mostly, illiterate people need help to comply with complicated procedures and the use of technology. So, instead of making banking seamless for many, it has also made banking a tiring process. Secondly, educating the employees of banks about the procedures of updated KYC can be a problem too. Employees who are old-fashioned and like to work in traditional ways might find themselves stuck. It might result in bad customer service and hurt the bank’s reputation. Thirdly, Cost is the main issue everywhere. Economic uncertainty and the ever-rising inflation are a big hurdle to implementing eKYC in many countries.
What is the future of eKYC in Banking?
Since the digital banking age began, technology has ruled over every banking process. Let’s take an example of a customer who needs to open up a bank account today. The first thing that banks will require is the necessary information to open up a bank account. Also, he may have to submit other supplementary documents too. Failing to comply won’t allow him to open his bank account. Similarly, the updated KYC and Anti-Money Laundering regulations are stricter than ever before. Banks, FIs, and other Fintech firms are now obligated to have a certain level of digitization in their KYC to combat rapidly evolving money laundering schemes.
Statista predicts that eKYC will grow and might dominate Manual KYC in the coming years.
- In 2022, the estimated market value for verification (e-KYC) from banks was over 1.3 million U.S. dollars.
- As of May 2023, 11,651 fintech firms launched their services in the Americas, making it the region with the most fintech startups globally. In EMEA (Europe, Middle East & Africa), 9681 setups were started whereas Asia observed 5061 new fintech startups.
Since fintech firms are the most potential clients of KYC and AML service providers, the above-mentioned statistics depict a rise in the demand for Digital KYC globally.
Conclusion
Digital identity and electronic KYC have revolutionized the banking industry. However, banks, FIs, and other fintech firms need to understand that efficient use of technology is essential. Training the employees at Fintechs and banks to implement Digital KYC is mandatory to make the customer onboarding experience truly seamless and effortless. Today, almost every working-class person or entrepreneur requires a bank account. KYC AML Guide navigates the users towards a futuristic approach that enables them to walk with the pace of time. Moreover, the security of everyone from Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing lies in full compliance with the KYC and AML regulations which is possible when the right KYC Vendor is selected.





