What is KYC (Know Your Customer)?
A standard definition of KYC is as follows:
Know Your Customer (KYC) is an approach applied by Financial Institutions (FIs) and other regulated entities for Customer Identification. It is a standardized and regulated compliance approach to verify the true identity of customers. Mainly, the purpose of KYC is to ensure customer safety and financial security.
Simply, an approach to KYC includes three steps:
- Establishing the Customer’s Identity
- Understanding the customer’s activities and ensuring legitimate funding
- Risk Assessment of Money Laundering and Fincrime.
In short, KYC ensures the onboarding of genuine customers and supports Anti-Money Laundering (AML) efforts.
Importance of KYC
The effectiveness of the KYC Process depends upon its ability to support the Anti-Fincrime approach. Globally, the threat of Money Laundering is rising exponentially. Money Launderers hide their illicit money through unrecorded channels. Hence, the true identity of the customer is key to combat Money laundering. KYC defines the compliance guidelines that are intensified as the threat increases. KYC (Know Your Customer) is becoming increasingly important and Stronger than ever.
Although, Banks and other financial institutions are regulating KYC globally. However, there is still a large gap between the regulation and implementation of KYC. Notably, regulators and firms are facing numerous challenges due to the economic crisis in implementing KYC. So, building a Risk-free financial model is required with an uncompromising KYC Process.
KYC Process: Foundation of Transparency
KYC is an ongoing process because of the continuous threats of Financial Crimes. There are 4 pillars of KYC that entail the process of KYC:
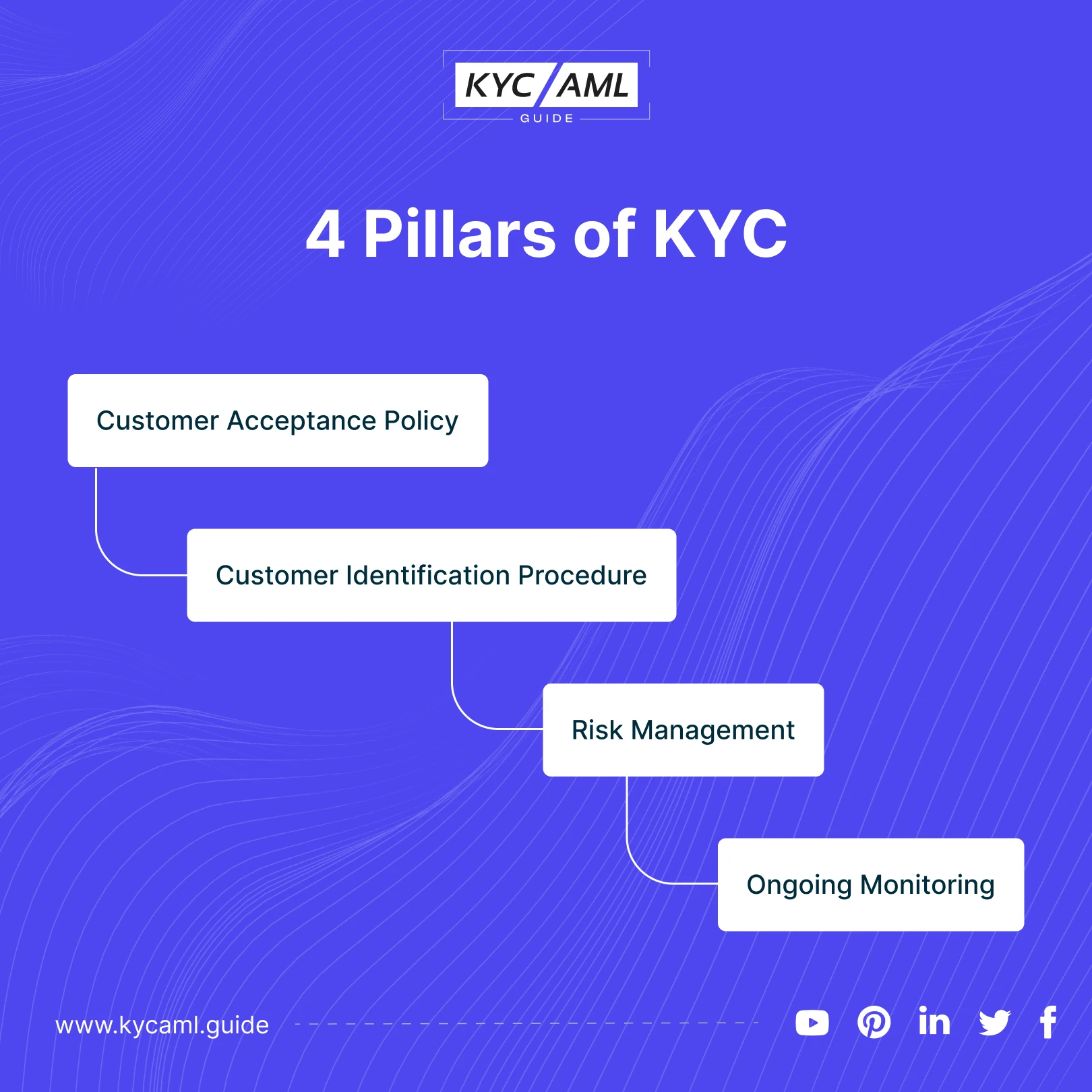
- Customer Acceptance Policy
- Customer Identification Procedures
- Risk Management
- Ongoing Monitoring
KYC Requirements
Since it is a compliance process, there are some requirements that customers need to fulfill while onboarding. The following are the basic KYC requirements:
- Proof of Identity
- Proof of Address
- Identity Card Verification
- Facial Verification
- Biometric Verification
- Document Verification
Apart from these, there can be other requirements based on the risk factors involved.
Types of KYC
With the rise in financial crime and compromised customer identities, the use of KYC heightened. Governments and regulators started refining and making their own ways to implement stringent KYC measures across the jurisdictions. Therefore, several types of KYC were formulated in order to tighten the grip on criminals. The types of KYC have their own pros and cons which are explained below.
| 1 | Document-Based KYC | Physical Documents are scanned, checked, and saved in the network to identify a customer. Passport, Driver’s license, and tax record are used for Documented KYC. |
| 2 | Digital KYC | When the KYC process is handled online, the ID verification also becomes digitized. This includes the submission of the digital photo ID of the customer’s identification documents. |
| 3 | Video KYC | Notably, it is one of the latest KYC approaches. Customers can now verify their Identity through online video recording via smartphones. Many banks and FIs now offer Video KYC through their Smartphone Applications. Mainly, Artificial Intelligence is used for Video KYC. |
| 4 | KYC In-Person | As the name suggests, In-person KYC (Know Your Customer) requires the customer to physically appear and confirm his identity. In-person KYC is required where the risk of forging identity is posed. |
| 5 | Biometric KYC | Undeniably, Biometric KYC is the most trending identification methodology today. Using Facial Recognition, Fingerprint, and Voice Recognition, biometrics is an evolution of the KYC process. |
KYC Regulated Industries
As we know, KYC is implemented almost everywhere now. Gradually, it is becoming one of the basic requirements in every walk of life. Specifically, a few High-Risk Industries in KYC require regulatory compliance. Mostly, a KYC Regulated Entity has notable traits that differ from regular industries.
Following are a few KYC Regulated Industries:

KYC Use Cases
Talking about the Use cases of KYC, we should know that the prime concern in using KYC is Financial Crime prevention. Also, KYC ensures a better insight into customer trends, and firms can make better marketing strategies. Following are the 5 main areas where KYC is applicable:
> Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance
Typically, KYC is used for the prevention of Money Laundering and is of high utility for MLROs. Since AML Compliance requires transaction monitoring and verification of identities, KYC (Know Your Customer) is of high importance here.
> Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
KYC is used for assessing the risks posed by a customer and for the regulatory requirements. CDD & EDD are the 2 main due diligence approaches based on the customer’s risk level.
> Fraud Prevention
KYC is also used in the prevention of Financial Fraud, Online Fraud, and Scams. It directly helps in the detection and prevention of fraudulent transactions and ensures a fraud-free and secure system.
> Regulatory Compliance
Mostly, international firms in the UK and the US are required to comply with regulations such as the USA Patriot Act, the EU’s AML Directives, and the Bank Secrecy Act.
> Customer Centric Decision Making
KYC proactively keeps the firm’s management informed about the trends and preferences of customers. Hence, this knowledge helps in gaining a competitive edge over competitors through early and informed decision-making.
Regulatory Framework of KYC (Know Your Customer)
Mainly, the Regulatory bodies for KYC include FinCEN, FATF, OFAC, and FCA. Apart from these, every country now has its own regulatory body to ensure KYC compliance. For instance, in China CBIRC and PBC regulate the KYC and AML regulations. Similarly, Russia has the FFMS and Bank of Russia for regulating the KYC/AML.
Closing Thoughts
KYC (Know Your Customer) is highly important in customer identity verification and prevention of financial crimes. Compliance with KYC is essential for secure and legal transactions and to prevent criminals from exploiting the financial ecosystem. With the ever-rising threat of money laundering and terrorist activities, the importance of implementing a KYC program increases for banks, financial institutions, and other firms. Even third-world countries have realized the importance of eKYC for seamless and secure transactions as it lies at the heart of fighting financial crime. Now, the world has entered the era of digitally operated financial systems, where advanced KYC and AML solutions stand as crucial guardians against the complexities of customer identification and seamless onboarding.
Learn more at KYC AML Guide and stay ahead in the compliance game for a secure financial future.





