What is a Multimodal Biometric Authentication?
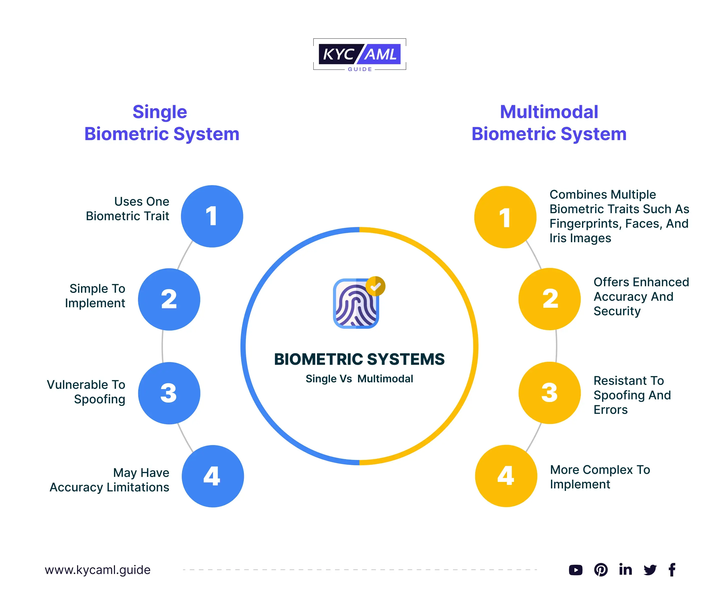
The multi-factor biometric authentication system combines two or more technologies that leverage the unique characteristics of distinct biometric technologies and data fusion technology to make the verification and identification process more accurate and secure. Just like your iPhone, you can unlock it with your face or fingerprint. The fundamental difference between a multi-biometric authentication system and a single-biometric system is that the multi-biometric authentication system can gather different biometric characteristics for example, a fingerprint biometric, facial biometric, or iris or retina scan, voice biometrics, handwriting recognition, and behavioral biometrics as well i.e. through independent or multiple collection methods.
A multimodal technique, a biometric identity verification system can thus provide four-layer biometric protection in a single step. It’s a straightforward but very secure consumer experience. Multimodal biometric authentication has the advantage of being a passive method that allows for ongoing authentication.
Examples of Multi-Modal Biometrics
- For authentication and identification, India’s Aadhaar employs a combination of biometrics such as fingerprint and iris. According to IBEF data, the ID is established based on the person’s biometric identity, therefore from August 2022, the data can be readily safeguarded against any form of fraud. 23.45 million e-KYC transactions have been performed, confirming Aadhaar’s confidence and security.
- Another example is a smartphone app that employs voice and facial recognition to authenticate user logins.
- A biometric access control system with a fingerprint scanner and a web camera for facial recognition is another example. If each user’s fingerprint cannot be obtained, this system will be able to employ the facial recognition capability
The Role of Multimodal Databases
To manage data from a single biometric identifier, such as a fingerprint or face, the same biometric database is utilized in traditional biometric systems. Implementing multi-factor biometrics, on the other hand, necessitates a complicated and heterogeneous infrastructure. Multimodal databases come into play here.
A multimodal database can manage various data and data models, including documents, key-value pairs, graphs, ranges, and relational data. It enables users to store and manage several forms of data in a single system without needing a separate database for each type. Compared to having various databases for different types of data, this enables greater flexibility, scalability, and ease of use.
One of the primary benefits of adopting a multi-modal database is that it gives a uniform and consistent method of managing and analyzing various types of data. A multi-modal database, for example, allows a company to store relational and document data in the same system and access and analyze both types of data in a consistent and integrated manner. This can ease data management and analysis while also reducing the time and cost of designing and implementing separate databases for each data type. Also, it can manage large amounts of data in real-time
What Advantages Does a Multimodal Biometric System Have Over a Single Biometric System?
Multi-modal biometric security with liveness detection makes stolen credentials and one-time passwords useless to criminals, reducing fraud losses by 90% or more.
The Rate of False Rejection is Minimal.
Unimodal biometrics are either confusing or ineffective in detecting demographics other than white males, and they are ineffective for a limited group, particularly black women, who have trouble using the system. Multi-modal biometric authentication systems minimize many of the difficulties presented by single-factor systems. This is accomplished by having the two components of biometrics collaborate to lower the false acceptance rate (FAR) where an error occurs) and the False Rejection Rate (FRR) where a person is rejected and not recognized by the system.
Secure
Individual biometrics can be easily faked or replicated by hackers, for example, face recognition systems can be tricked by a convincing image of the individual. A drawback of a biometric system is a lot of false acceptance rates. The multimodal system is also more secure because two biometrics are more difficult for hackers to compromise than one.
Flexible
Unimodal systems can also encounter non-real-world issues when the biometrics utilized are damaged by disability or disease, and the power mode of the device to read biometrics is a critical issue. This can result in a significant number of false positives. This approach is also more user-friendly than unimodal biometrics because it is easier to overcome data noise. If there is a cut on the fingerprint from an injury, another biometric identification i.e. voice can used to compensate for it.
Spoofing Errors
The Unimodel System Biometric traits are exploited to prevent identification. It is feasible to develop an artificial biometric pattern that assumes another person’s identity. An attacker, on the other hand, cannot utilize false biometric data that is very relevant or accurate for multi-modal biometrics.
Acceptance
Multimodal biometric authentication systems have much higher rates than single biometric identification systems. Because many users may have privacy issues regarding face recognition, they can employ internal vein recognition, which does not generate privacy concerns.
Operational Efficiencies
Replacing old passwords, KBA, OTP, and other security techniques with multimodal biometrics can have a substantial influence on fraud operations, decreasing the financial footprint of the increasing payment sector. Financial organizations can minimize call center costs, fraud alert systems, and fraud volumes by enhancing trust with advanced multi-modal biometrics.
Which One of the Following is Not an Advantage of Biometric Systems?
The drawbacks of biometric systems are
Costs
Multi-mode systems cost significantly more than single-mode systems. The system itself, the computer power necessary to run it, and multimodal database storage to record biometric data may all incur costs
Verification
There is also the possibility of consumers becoming entangled in authentication processes. However, this is no different than the usage of multi-factor authentication to gain access.
Non-Universality
Multimodal systems, like unimodal systems, can have the problem of not being universal if the biometric data used is compromised by disability or disease
Environmental Impact on Multimodal Systems
Similarly, the environment can still affect multi-modal biometric systems, as it can affect the system’s capacity to recognize an individual. For example, lighting, posture, and facial expression all affect the accuracy of face recognition, introducing noise into the data. The presence of environmental noise in the data can have an impact on the measured biometric data. It can, however, also have an impact on unimodal biometrics.
Bias
Bias is one of the issues that even the most robust identity verification methods, such as multimodal biometrics, face. Algorithms are not biased but the individuals who control the data fed into the machines can incorporate bias into the training process. A facial recognition system trained on photos with disproportionate demographic attributes to the actual population may struggle to recognize faces from underrepresented demographic groupings. Bias will become less of an issue when biometrics become more extensively utilized and more variants are captured and included in public databases.
Why are Biometrics used in Security Systems?
Technological advancements, the rise of cyber threats, and the failure of user password authentication systems have all contributed to the emergence of biometrics. Furthermore, the digitalization of traditional banking, capital markets, and insurance, as well as the rise of e-wallets, have altered the global business landscape. The risk, however, increases as the digital attack surface expands. Banks are using biometrics to decrease identity fraud, establish audit trails, and protect financial data.
As a result, several banks use multimodal biometric KYC, which incorporate the results of multiple biometrics traits.
- Geolocation and facial recognition capabilities are available for the access control machines. In addition to visual checks, your bank’s security system may request voice-based authentication along with eye patterns. This way, even if one of the data points is compromised, you can prevent spoofing.
- Biometrics also allows for continual background checks to confirm that the appropriate individual is completing a critical transaction, increasing transaction monitoring.
- Biometrics can eliminate dependency on cards, PINs, and passwords, boost trust by giving account access, and create new business opportunities in locations where individuals lack access to financial services or identity documents.
- By providing remote alternatives, multimodal biometric authentication can also speed up KYC onboarding. With a few clicks, customers can open bank accounts, e-wallets, business applications, loan applications, and insurance. Biometrics and digital currency exchanges are assisting the globe in meeting its investing objectives.
Also read: What is Digital Onboarding and How It Works?
With multi-factor biometric authentication technology, small, medium, and large enterprises may strengthen their security posture, stay ahead of their competition, and limit the possibility of unauthorized access. To save the manual burden, new advanced biometric security options can be integrated into workplace attendance and check-in systems. Access to control systems with facial recognition and fingerprint readers, on the other hand, prevents identity fraud. To improve security, members can integrate fingerprint, facial recognition, and even iris scanners.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that authentication is accomplished in a variety of methods. Biometrics is the most widely used authentication mechanism. The increased requirement for security has resulted in a superior system called a multimodal biometric authentication system, which has replaced the simple unimodal systems that were previously used for biometrics and often comprised only one biometric feature for authentication. Multimodal biometric systems employ a variety of biometric features, making them more safe and adaptable to various biometric parameters.
The KYC AML Guide’s Vendor Analysis Consultancy provides complete analysis and experience in selecting and deploying multimodal biometric solutions for increased KYC and AML compliance. You can also use our CaaS marketplace for identity and access management (IAM) consulting.





