What is Biometric Voice Recognition?
Voice recognition was first used in banking in 2014, and it is now rapidly gaining popularity in consumer electronics, medical diagnostics, and finance services. The process of determining an individual’s identity verification using their unique voice characteristics is known as biometric voice recognition. Unlike traditional methods that require physical input, such as passwords or logos, voice recognition is based on the unique characteristics of a person’s voice. It enables two-factor authentication by combining voice biometrics with an identification credential such as an ID, password, or PIN, granting access to secure locations, facilities, and resources.
The speech and voice recognition market is expected to reach $56.07 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 19.1% between 2023 and 2030. KYC is critical in biometric voice recognition because it ensures the accurate verification of customer identities, thereby improving the security and trustworthiness of voice-based authentication systems.
Recent advances in neural network technology have resulted in the creation of biometric identity verification systems that are not only faster, but also faster than their competitors. These systems require fewer speech samples to accurately identify each individual, which broadens their applications.
Voice Biometrics vs. Voice Recognition
In the realm of voice-related technologies, voice biometrics and voice recognition serve distinct functions. Voice biometrics focuses on the distinct characteristics of a person’s voice to reliably identify and authenticate them. Its primary application is in security settings, where it ensures user privacy and authorizes access to confidential data, such as during login procedures, financial transactions, or interactions with call center services.
Voice recognition, on the other hand, is intended to convert spoken language into text that computers and digital devices can process. This technology underpins virtual assistants such as Google Assistant, Alexa, and Siri, allowing users to perform tasks and gather information using voice commands. Speech recognition is used in personal assistant applications as well as in the healthcare industry for quick transcription.
Regulations Governing Voice Recognition Technology
Voice recognition technology in the United States is governed by common law mandates, data destruction laws in over 30 states, data breach notification laws in all 50 states, and vendor contract statutes. These rules differ, emphasizing the importance of staying informed for users, developers, retailers, and manufacturers.
- European Union’s GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
- BIPA (Biometric Information Privacy Act)
- COPPA (Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act)
How does Voice Recognition Biometrics Work?
Biometric Voice recognition technology has advanced significantly, with accuracy rates exceeding 95% in some cases, and up to 99% in others. Conventional passwords, on the other hand, are significantly less secure, with only 80% providing even minimal security. The voiceprint is as unique as iris or fingerprint recognition, making it nearly impossible to duplicate. The ISO/IEC 30107-11 standard defines an architecture that is used to provide the highest level of trustworthiness when verifying user identity.
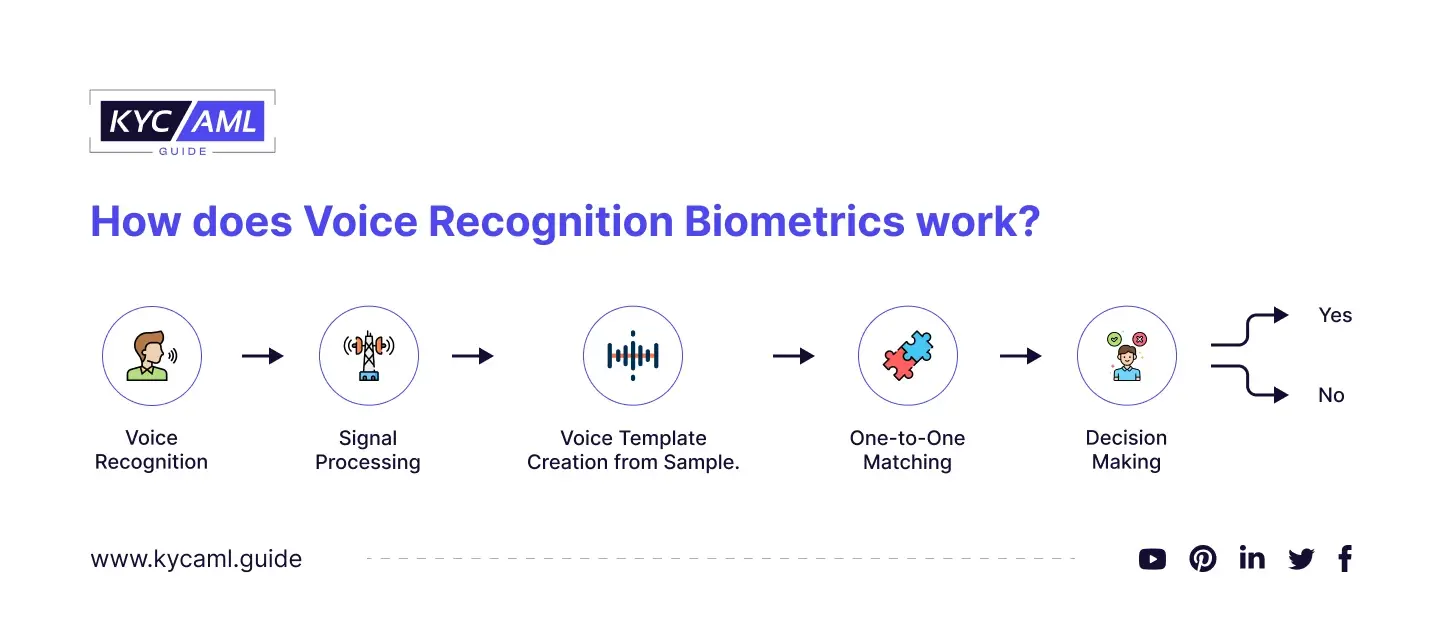
- Voice recognition captures the human voice to produce a distinctive voice print.
- This voice print is generated by software that distributes the voice across multiple frequencies.
- Text-independent recognition and Text-dependent recognition are the two main types of voice recognition. Text-independent recognition allows for meaningful speech. It is highly practical and adaptable. Text-dependent recognition requires the repetition of a single sentence, imposing a speech content limitation but providing an extra layer of security.
- A sample is created from a volume sample and is proprietary to the authentication system.
- The system compares a newly provided voice sample to the original template to authenticate a person’s identity. A strong match between templates indicates that both samples were spoken by the same person, confirming their identity. This is referred to as one-to-one matching.
- Voice recognition can also perform one-to-many matching in some cases. To find a match, a voice sample from an unknown identity is compared to multiple enrollment templates. While speaker identification is commonly used, its accuracy varies depending on the application.
Biometric Recognition Technology Pros and Cons
The Pros of Biometric Voice Recognition:
Operational Efficiency:
Simplifies verification, reducing the need for costly manual checks.
Improved User Experience:
Removes the burden of remembering passwords and answering security questions, resulting in higher customer satisfaction.
Increased Accuracy:
Offers greater reliability than passwords because voices are unique and difficult to replicate.
Simple Integration:
Often integrates seamlessly with existing systems, streamlining implementation.
Improves Customer Experience:
Allows for quick and painless authentication, increasing user satisfaction.
Boosts Security:
Increases security by mitigating breaches caused by compromised or lost passwords.
Instant User Identification:
Identifies users and customizes interactions in real time.
Automation:
Increases efficiency by automating business-to-customer interactions.
Productivity Gains:
IT staff is freed from time-consuming user verification and password updates.
Two-Factor Authentication:
This can be used as part of a two-factor authentication process to increase security while minimizing complexity.
The Cons of Biometric Voice Recognition:
Voice Cloning or Spoofing Attacks:
Advanced cyber attacks such as “voice spoofing” attempt to mimic a user’s voice. Concerns have been raised about voice recognition systems being vulnerable to voice cloning or spoofing attacks, which frequently use AI-generated synthetic voices, raising privacy concerns.
Accuracy Issues:
Some accuracy issues persist, particularly when it comes to verifying people’s identities. Voice recognition may not be as accurate as other biometric methods, such as facial recognition.
Voice Variability:
People’s voices can change over time or due to factors such as respiratory illnesses, allergies, vocal cord injuries, and other conditions can all cause a user’s voice to change and affect recognition.
Noise Sensitivity:
Authentication can be difficult in noisy environments with a lot of background noise. Factors such as loud background noise, static, or poor connections can degrade the quality of audio samples.
Liveness Detection:
It is required to ensure that the speaker is a real person and not a recording.
Privacy Concerns:
There are ethical and safety concerns about devices that may capture users’ communications.
Biometric Voice Recognition in Security System
Platforms such as Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube can give fraudsters access to voice data, but obtaining sensitive account information remains difficult.
Banks are using biometric technologies such as voice recognition in ATMs, and mobile and in-branch banking with additional security measures to combat voice spoofing threats and to improve transaction security. Behavioral analysis, device identification, geolocation analysis, time-based analysis, and fraudulent pattern analysis are some examples. When high-risk activity is detected, banks should use step-up authentication to ensure the user’s authenticity.
According to Juniper Research, mobile biometrics will process approximately $2 trillion in in-store and remote payments annually by the end of 2023, which is 17 times more than the $124 billion expected in 2018.
Notably, financial institutions such as the Royal Bank of Canada are using voice biometrics to authenticate users before allowing ATM transactions. This method requires users to provide both a PIN and a voice sample, which contributes to the market’s growth in North America over the forecast period.
According to a Finextra report, “the UK bank reckons its voice biometrics system has prevented almost £249 million of customers’ money from falling into the hands of telephone fraudsters in the last year.”
AI advancements have propelled voice biometrics to the forefront of modern contact center technology. It provides numerous advantages, including increased security, fraud prevention, data protection, improved customer experiences, and shorter average call handling times.
Conclusion
Biometric voice recognition technology is gaining popularity across industries because it provides secure user identification through unique voice characteristics. While it improves security and user experience, there are some drawbacks, such as potential vulnerabilities to voice cloning and accuracy issues. It is critical in the financial sector for KYC/AML compliance, as well as transaction security.





