In this age of sophisticated cyber threats, practical knowledge and tactics to defend oneself from mistaken identification are essential. This comprehensive blog investigates the severity of identity spoofing and spoofing attacks, explains how they work, and, most significantly best practices to prevent them.
What is Spoofing?
The term “spoofing” dates back to the 1800s and refers to any deceitful or fraudulent act. Nowadays, spoofing refers to a sort of cybercrime in which fraudsters change their identities to deceive innocent individuals.
A spoofing attack is a type of cyber attack where an intruder imitates another legitimate device or user to launch an attack against the network. In other words, an attacker sends a communication from a device disguised as a legitimate device. Spoofing attacks have allowed countless cyber criminals to breach enterprise networks covertly without being detected.
A spoofing attack is a type of cyber attack in which an attacker pretends to be another genuine device or user to initiate an attack against the network. In other words, the attacker transmits a valid communication from the encryption device. Many fraudsters have used cyber attacks to inadvertently breach company networks without being discovered. Scammers target various Internet communication platforms. All spoofing attacks use some form of social engineering. Spoofing attacks can manifest themselves in a variety of ways, including fake emails, IP spoofing, DNS spoofing, GPS spoofing, website spoofing, etc.
A prominent example of a social engineering scam is the grandchildren scam. The elderly are the most common victims of this scam since they are less tech-savvy and are ignorant of the warning signs. According to the Canadian Anti-Fraud Centre (CAFC), seniors who fell victim to such schemes lost more than $9.2 million in 2022, up from $2.4 million in 2021.
Surprisingly, Microsoft estimates that attackers spend an average of 146 days on the network before being found. This demonstrates that the scammers have adequate time to obtain the critical information. Ignoring these attacks can have disastrous consequences. It is estimated that cybercrime costs businesses more than $1 billion per year.
What is Spoofing in Cyber Security?
Identity spoofing is a growing cybersecurity threat. Identity spoofing is a technique for impersonating or falsifying the identity of a person or organization to obtain access to confidential data or information, commit fraud, or engage in illegal or destructive behavior. This is also known as identity impersonation or forging.
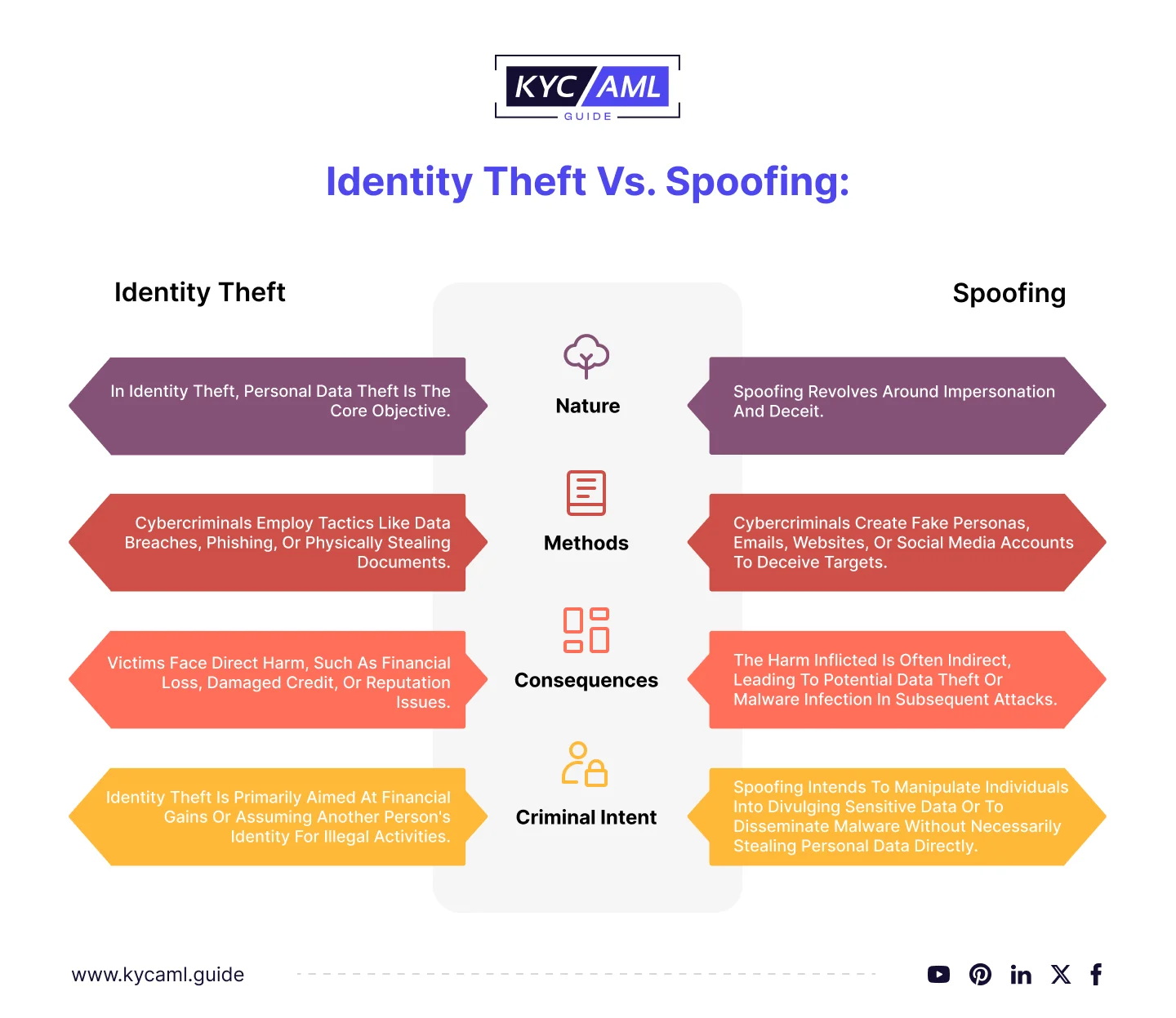
The key differences between Identity theft and Spoofing are
Also read: The Role of Cybersecurity in KYC and AML Compliance
Techniques of Identity Spoofing
There are many types of identity spoofing attacks. Some of them are as follows
Document spoofing
The analysis of the identity document is usually the initial step in the digital onboarding procedure. In this instance, it is critical to have technology that can detect the most common types of document fraud, such as photocopying, screen attacks, data manipulation on papers, and the display of high-quality false documents.
Caller ID Spoofing
Caller ID spoofing is the practice of altering the phone number displayed on the recipient’s caller ID display so that it appears to be a trustworthy caller. This can be used to dupe the receiver into divulging personal information or to launch a phishing attack.
IP Address Spoofing
IP spoofing is the process of masking an attacker’s IP address so that it appears to be from a trustworthy source, such as a company’s internal network. This can be used to get access to sensitive data or to launch denial-of-service attacks.
Website Spoofing
Website spoofing is the practice of creating a bogus website that appears to be authentic to deceive consumers into revealing personal information. This can be accomplished by adopting a similar domain name or by replicating the design of a legal website.
Email Spoofing
Email spoofing is another prevalent type of spoofing attack. This occurs when a scammer sends an email with a forged sender address to infect your device with malware. These bogus email accounts frequently spoof someone you know, such as a family member or coworker.
Text Message Spoofing
Did you know that you may spoof SMS messages by using a different phone number? Text message spoofing is another cybersecurity threat that occurs when a fraudster sends a text message while concealing their identity with an alphanumeric sender ID.
Biometric Spoofing
Biometric spoofing is any technology that allows a fraudster to circumvent biometric data validation and impersonate another individual. Using a forged fingerprint to unlock a device, for example, is an example of biometric spoofing. The following are examples of biometric spoofing.
Facial Biometrics Spoofing
One critical step in the identity verification or authentication process is biometric comparison, which requires users to take a selfie and compare their face to the one on the ID. In these circumstances, numerous spoofing methods or presentation attacks are used to mislead facial recognition systems. Some of them are as follows

- Print attacks involve intercepting or manipulating documents by exploiting printer vulnerabilities.
- A video replay attack occurs when someone attempts to fool a live system by displaying a video and acting as if the video is a live person.
- A 3D mask attack is one in which an attacker produces a three-dimensional physical mask to mislead facial recognition systems.
- A thermal imaging attack is a method of exploiting thermal emissions of electronic devices to gain unauthorized access or extract sensitive information
- An impersonation attack is a type of cybersecurity spoofing attack where an attacker pretends to be a different individual, entity, or system to deceive others and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or resources.
- Camera manipulation refers to various techniques used to tamper or manipulate the output of a camera or its functionality.
- An artificial iris attack is in which an attacker deceives iris recognition systems by using a synthetic or created iris pattern.
- A gaze manipulation refers to techniques used to influence or control the direction or focus of a person’s gaze.
- A virtual reality attack takes advantage of virtual reality (VR) technology.
- A deepfake attack is the use of deepfake technology using AI to generate videos that misrepresent someone else.
- A makeup attack occurs when a person alters their look with cosmetics or other tactics to dodge or deceive facial recognition systems.
- Attackers employ very convincing masks to imitate someone else, typically with malicious intent, in hyper-realistic mask attacks.
- Face swaps are a popular form of identity theft in which individuals or attackers use software or procedures to replace one person’s face in a picture or video with another person’s face, resulting in a convincing but misleading portrayal.
Voice Biometrics Spoofing
Biometrics systems are vulnerable to assaults that use pre-recorded or synthetic voices. Again, having a system that can detect these fraudulent efforts is critical.
Environmental Manipulation
The deliberate alteration or modification of the physical or technological environment to support or exploit security vulnerabilities is known as environmental modification. This includes tampering with various aspects of the environment to obtain unauthorized access, compromise systems, or harvest sensitive information.
Smudge Fingerprint Attack
It is a sort of biometric spoofing attack that targets fingerprint sensors on touchscreen devices. This entails smearing or smudging the fingerprint sensor’s surface with oil, sweat, or other substances to change the original fingerprint and make it harder for the sensor to correctly recognize a person’s fingerprint.
How does Identity Spoofing Occur?
Spoofing attacks frequently jeopardize an organization’s identity verification process, particularly during customer onboarding and authentication. Customers must present proof of identity throughout the KYC process before they may log in to prevent financial fraud.
Let us begin by looking at the features of an Identity spoofing attack. Consider a banking app that enables customers to access security by employing facial recognition technology to swiftly and conveniently access their accounts.
The steps of a spoofing attack are:
- The fraudster selects a target user and gathers public photographs and videos of that person from the Internet.
- The fraudster uses advanced deepfake technology to make a realistic and convincing video of the target’s face. Deepfake involves precise facial movements, expressions, and voice motion replication.
- The attacker downloads the app and attempts to log in with facial recognition utilizing deepfake video.
- Fake videos are used to fool mobile app facial recognition system
- As a result, the fraudster gains unauthorized access to the target’s account.
As demonstrated by the example, fraudsters may attempt to circumvent security measures throughout the inspection process to get personal information about your organization or customers.
According to Reuters, about 500,000 video and audio deepfakes will be published on social media worldwide in 2023. Deepfakes continue to be a major worry for the cryptocurrency business, with 70% citing their growing popularity among fraudsters.
It can seem frightening, but there is no need to be concerned. In the following part, we will discuss how to quickly prevent this type of identity spoofing attack.
How to Prevent Identity Spoofing?
Although identity spoofing can not be permanently limited, there are some precautions you can take to limit identity spoofing attacks and malicious spam.
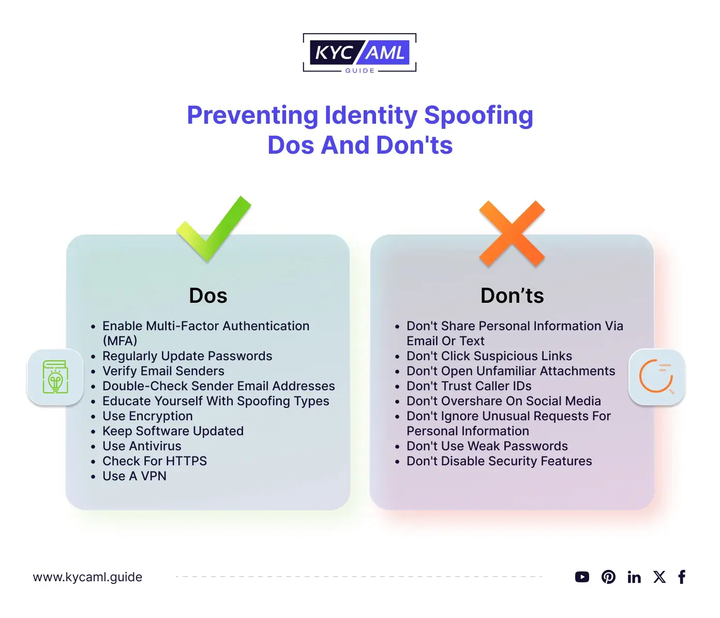
The do’s and don’ts to prevent spoofing attacks in cybersecurity are as followsMake Use of the Identity Verification Service
Identity verification services are an efficient way to avoid counterfeiting. To ensure that a person or organization is who they say they are, these services frequently use a combination of KYC document verification, biometrics verification, and other approaches.
Also Read: MRZ Code: A Reliable Tool for Identity Verification
Document Spoofing Prevention
Use a digital identity verification software, visit KYC Solution Directory, which automates identification document scanning for fraud detection by utilizing optical character recognition (OCR) technology. NFC-based authentication uses RFID chips to retrieve data from identity documents, protecting against counterfeiting and boosting security. These practices assure compliance with KYC rules while also making customer onboarding easier.
Biometric Spoofing Prevention
Use biometric verification, such as selfie verification, in which clients take selfies that are compared to the photo on their ID cards. It incorporates liveness detection, which requires users to do specific behaviors to demonstrate their physical presence. These safeguards dramatically lower the possibility of biometric spoofing while also improving overall identity security.
For professional advice on identity verification, you can consult the KYC AML guide for expert guidance on identity verification by using our service of KYC technology buying. Organizations can successfully avoid identity spoofing and fraudulent activity by employing these advanced verification methods while remaining in line with KYC/AML rules.
Also Read: Multi-Modal Biometrics for Enhanced Authentication
Bottom line
In an age of ever-evolving cyber threats, the protection of identity is of utmost importance. Identity spoofing poses significant risks to individuals and organizations. According to the UK Government’s Cyber Security Breaches Survey 2022, 83% of companies experienced a cyber threat in the previous year due to phishing. Applying strategies such as identity verification services, advanced document scans, and others is crucial to protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with KYC/AML regulations.





