Introduction
Sectoral sanctions are a critical aspect of international economic policy, often employed by countries or groups of nations to target specific sectors or industries within a targeted nation. These sanctions serve various foreign policy objectives and have a significant impact on global commerce.
This blog will delve into the intricacies of sectoral sanctions, exploring their purpose, implementation, and impact on various countries. Additionally, it will highlight the crucial role of KYC and AML compliance in aligning with sectoral sanctions enforcement, ensuring robust due diligence, and mitigating risks for financial institutions.
Understanding Sectoral Sanctions
Sectoral sanctions are different from other sanctions worldwide which act as targeted economic sanctions imposed by one country or a group of countries (registered under a licensed regulatory body) on specific sectors or industries within a targeted country. Sectoral sanctions are often used as a foreign policy tool to address specific concerns or to force the targeted country into changing its behavior without resorting to a full-scale economic embargo or trade blockade.
Purpose of Sectoral Sanctions
The purpose of sectoral sanctions is to apply targeted economic pressure on specific sectors or industries within a country’s economy to achieve sovereign policy objectives such as influencing its government behavior, addressing national security concerns, responding to human rights violations, promoting the rule of law, mitigating economic harm, creating leverage for diplomacy, and fostering international cooperation while minimizing collateral damage to civilian populations and non-targeted sectors.
What is the Sectoral Sanctions Identifications List (SSI)?
OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets & Control) published a list called the SSI list as of 14 September 2023 to identify the persons operating in different sectors of the Russian economy. The list is not a direct subset of a larger and broader list called the SDN (Specially Designated Nationals) list but individuals and companies may appear in both lists at the same time. The SSI list specifically includes individuals and entities that are subject to sectoral sanctions imposed by the United States. These sectoral sanctions target specific sectors or industries within a country’s economy and restrict certain transactions with entities on the list. The SSI List is designed to help U.S. persons and businesses comply with these sanctions by identifying the individuals and entities that are subject to these restrictions.
Major Countries Under Sectoral Sanctions
Here is a list of famous Sectoral Sanctions imposed by the US, UN, and the EU on different countries.
| 1 | Russian Sectoral Sanctions (by US & EU) | In response to the illegal war waged by Russia in Ukraine, the United States and the European Union imposed different sanctions including sectoral sanctions on Russia starting in 2014 and intensifying the sanctions in September 2023. The main targeted sectors are finance, energy & defense. |
| 2 | North Korea Shipping Sanctions (by UN & US) | The United Nations and the United States have imposed sectoral sanctions on North Korea’s shipping industry starting in 2017. These sanctions target vessels, shipping companies, and related entities involved in North Korean illicit activities, such as smuggling and sanctions evasion. |
| 3 | Afghanistan Banking Sanctions (by the US) | President of the US Joe Biden signed an Executive Order on 11 February 2022 which restricts ‘Da Afghanistan Bank’ technically freezing all assets in the US. This presidential document is issued as a part of sectoral sanctions on Afghanistan to prevent the national security threat by the latest ‘Taliban Takeover’ since 2021. |
| 4 | Iran Additional Sectoral Sanctions (by the US – 2020) | Under the presidency of Donald Trump, Iran faced additional sectoral sanctions mainly on mining, construction, manufacturing, textile, and other sectors to prevent the National Security threat. |
Furthermore, the Sanctions Program & Country Information contains information related to sanctioned countries under the OFAC sanctioning guidelines. This list is updated whenever the United States Government imposes sectoral sanctions or any other sanctions on a country.
The Difference between Sectoral Sanctions and Other Sanctions
| Aspect | Sectoral Sanctions | Targeted Sanctions |
| Target Scope | These sanctions target specific sectors or industries within a country’s economy, such as finance, energy, technology, or defense. | Traditional sanctions, aim to restrict a wide range of economic and trade activities with a targeted country. Virtually, they encompass all sectors of the targeted economy. |
| Precision Level | Sectoral sanctions are more precise in their targeting. They seek to minimize the impact on civilian populations and non-targeted industries while focusing pressure on the specific sectors associated with objectionable activities. | Traditional sanctions can have a broad and indiscriminate impact on an entire country’s economy, affecting both the targeted government and ordinary citizens. They may refer it to as collateral damage. |
| Objective | To encourage a targeted country to change its behavior in a particular area, such as human rights violations or regional aggression. | It includes regime change, the cessation of a specific conflict, or the achievement of broader foreign policy goals. |
| International Coordination | While international coordination can be important for sectoral sanctions, they are often implemented by a smaller coalition of countries or unilaterally by one country. | Traditional sanctions are more likely to involve a broader international coalition or be authorized by international bodies like the United Nations. |
| Enforcement and Monitoring | Effective enforcement and monitoring are crucial, but the scope is narrower, making it potentially more manageable. | Enforcing comprehensive sanctions across a wide range of economic activities and sectors can be more challenging and resource-intensive. |
| Effectiveness and Response | The effectiveness of sectoral sanctions can vary depending on various factors, including the targeted country’s resilience and willingness to change its behavior. | The impact of comprehensive sanctions can vary widely and may have broader diplomatic, economic, and humanitarian consequences. |
Common Sectors Targeted by Sectoral Sanctions
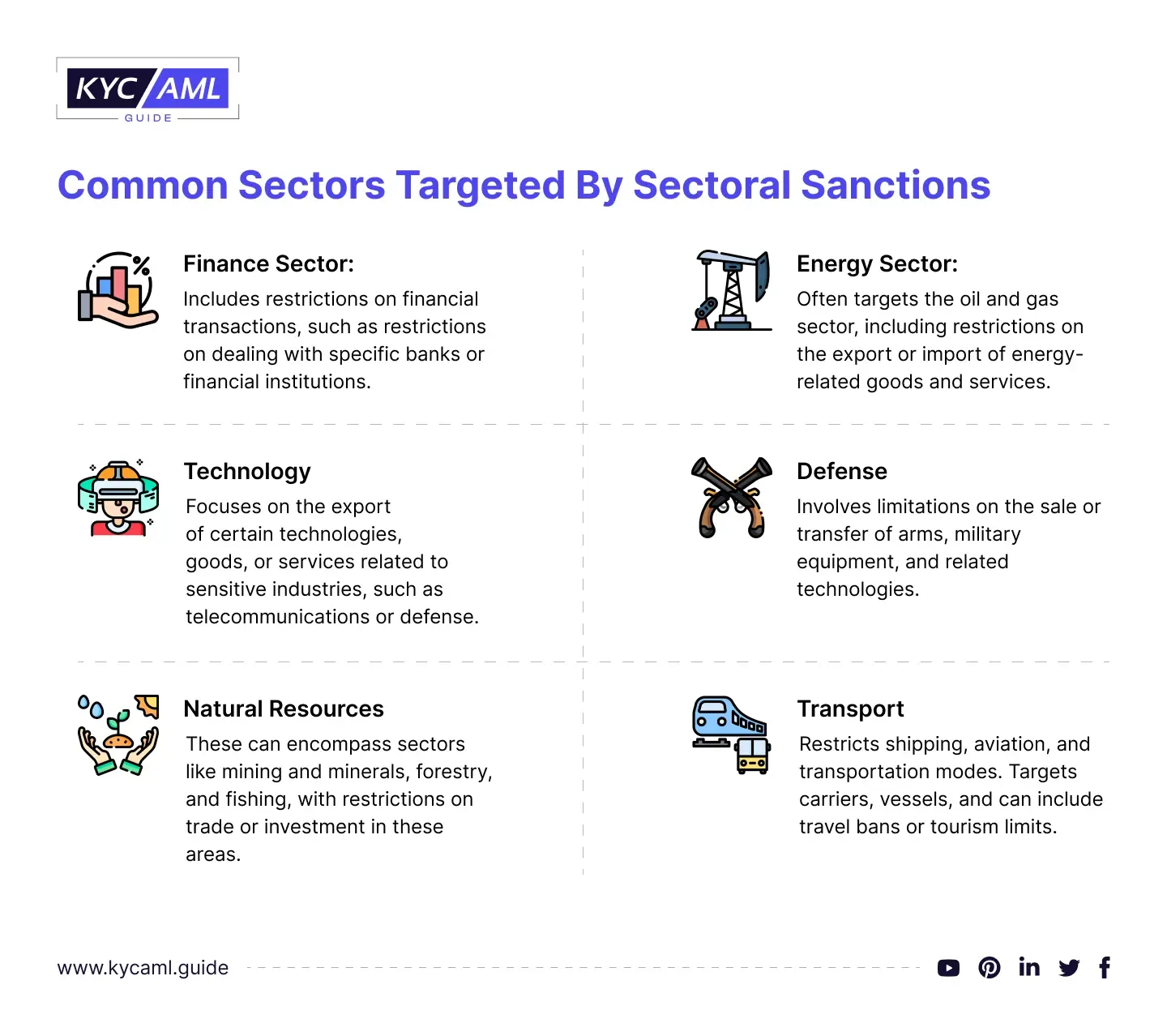
- Finance Sector: Includes restrictions on financial transactions, such as restrictions on dealing with specific banks or financial institutions.
- Energy Sector: Often targets the oil and gas sector, including restrictions on the export or import of energy-related goods and services.
- Technology: Focuses on the export of certain technologies, goods, or services related to sensitive industries, such as telecommunications or defense.
- Defense: Involves limitations on the sale or transfer of arms, military equipment, and related technologies.
- Natural Resources: These can encompass sectors like mining and minerals, forestry, and fishing, with restrictions on trade or investment in these areas.
- Transport: Restricting shipping, aviation, and other transportation modes. The main targets are carriers, and vessels and can include travel bans or tourism limits.
These sectors play a crucial role in developing a country’s economy and so they are targeted to create the maximum pressure on it.
The Role of OFAC in Global Compliance
On behalf of the US government, OFAC is a regulatory body empowered to impose sanctions on almost all countries in the world that pose a threat to the national security of the American people. With a profound role in Global Compliance, here are some of the aspects of OFAC’s role:
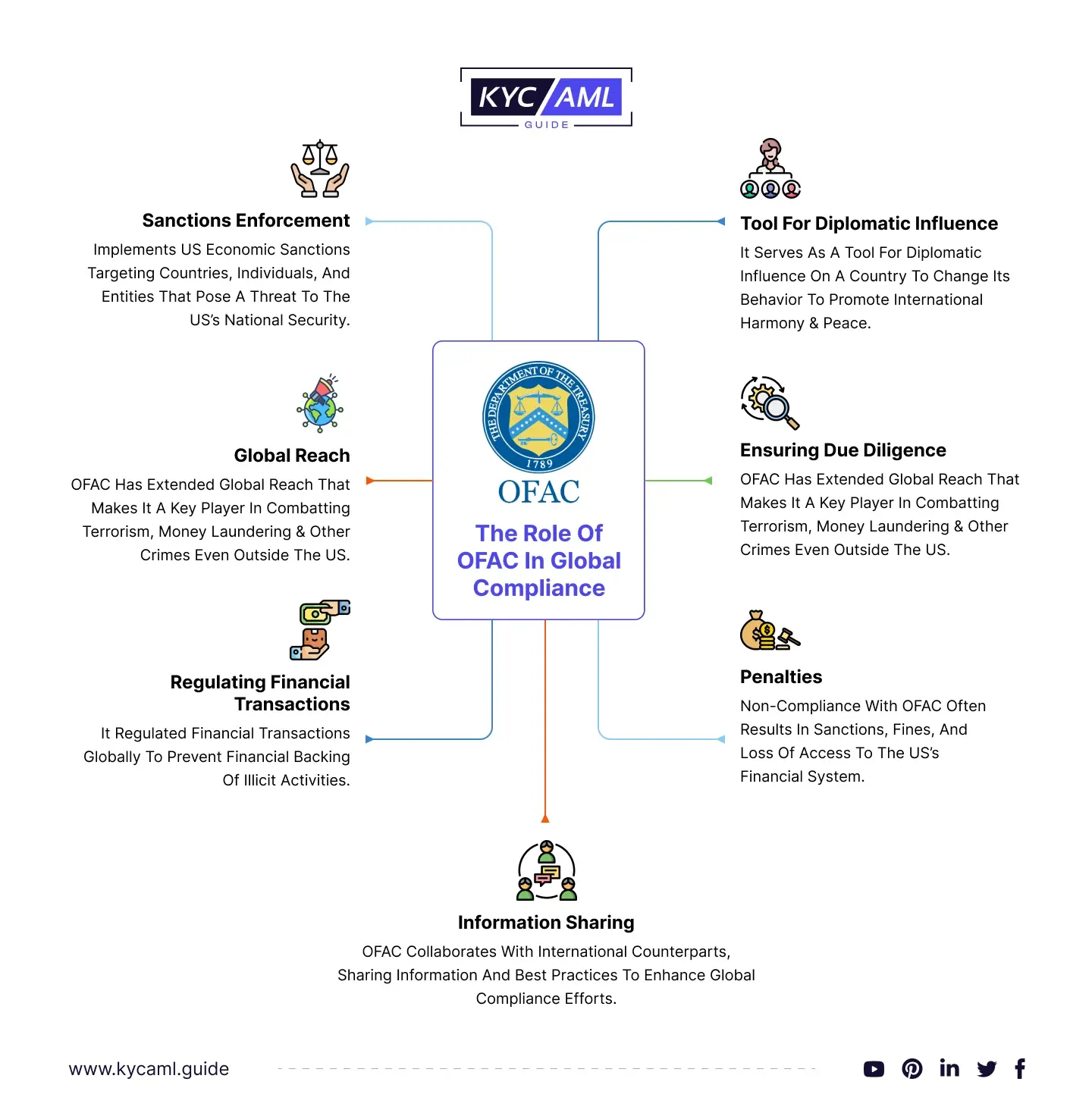
- Sanctions Enforcement: Implements US economic sanctions targeting countries, individuals, and entities that pose a threat to the US’s National Security.
- Global Reach: OFAC has extended global reach that makes it a key player in combatting terrorism, money laundering & other crimes even outside the US.
- Regulating Financial Transactions: It regulated financial transactions globally to prevent financial backing of illicit activities.
- Tool for Diplomatic Influence: It serves as a tool for diplomatic influence on a country to change its behavior promoting international harmony & peace.
- Ensuring Due Diligence: Companies avoid engaging with sanctioned entities and persons under OFAC’s compliance through strong Due Diligence.
- Penalties: Non-compliance with OFAC often results in sanctions, fines, and loss of access to the US’s financial system.
- Information Sharing: OFAC collaborates with international counterparts, sharing information and best practices to enhance global compliance efforts.
Considering sectoral sanctions, OFAC imposes them on the main sectors in countries whose practices are against the interests of the US.
The Importance of KYC and AML Compliance
Financial institutions play a pivotal role in preventing illicit financial flows (IFFs) by implementing due diligence, transaction monitoring, sanctions compliance, and reporting mechanisms. They serve as the frontline defenders of the global financial system, ensuring that funds entering and exiting are legitimate, thereby thwarting money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities that undermine economic stability and security worldwide. In this regard, KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) processes align with sectoral sanctions enforcement in the following ways:
- KYC and AML procedures help in the identification of customers, their business activities, and any suspicious activity linked to them.
- Both KYC and AML incorporate screening against sanction lists such as SSI lists by OFAC that help FIs in blocking transactions to strengthen the enforcement of sectoral sanctions.
- While dealing with high-risk identities, KYC and AML procedures require Enhanced Due Diligence to conduct deeper checks to identify any links to the sectoral sanctioned entities or persons.
- Transaction Monitoring in KYC and AML systems helps in detecting any transactions to and from a sectoral-sanctioned country, entity, or individual. This includes suspicious activities, and ensuring OFAC compliance of the financial institutions.
- Moreover, the KYC and AML procedures mandate robust risk assessments, documentation & reporting and cultivate compliance culture throughout the FI.
Risk Mitigation Through KYC AML Guide
Staying updated and compliant with regulatory requirements like OFAC’s is mandatory to prevent financial crimes and engaging with risky identities. For this purpose, financial institutions need to make informed and cost-efficient decisions while choosing their KYC vendor. KYC AML Guide offers its exclusive consultancy services with concrete industry knowledge & experience to cultivate a culture of robust compliance worldwide. Sectoral sanctions are a major concern for banks and FIs where clients face numerous challenges in staying compliant.
Challenges in Regulatory Compliance
Firstly, Fintech firms are required to stay updated with the ever-changing regulatory landscape. Especially when operating in multiple jurisdictions the situation becomes more complex and difficult to tackle. Secondly, identifying the beneficial ownership & ultimate beneficiaries with billions of identities in the database requires robust KYC and AML measures where fintech firms can’t spend extravagantly without thorough research in selecting their KYC or KYB (Know Your Business) partner. Thirdly, the risk of getting penalized and facing reputational damage due to non-compliance is a risk to the financial integrity & public trust.
Best Practices for Effective Compliance
Apart from the ongoing best practices in KYC and AML Compliance, fintech firms need to improve their compliance adherence by using advanced KYC tools. For this, the choice of KYC vendor can make a visible difference in improving compliance practices. KYC vendors ensure that the firm’s operations and financial practices align completely with the most updated AML regulations. This includes adherence to guidelines by OFAC to avoid sanctions through process automation in screening, monitoring, and reporting processes under KYC and AML. Here are a few attributes that Fintech a trusted KYC partner offers to Fintech firms:
- AI-based screening for enhanced accuracy and speed in filtering out identities from different databases like sanction lists, watch lists, and PEP lists.
- Enhanced Due Diligence ensuring a risk-based approach including beneficial ownership analysis & sources of fund verification.
- Global Compliance and coverage would encompass the global sanction database and regulatory database to address the international nature of fintech operations with respect to regulatory compliance.
- Vendor Due Diligence is another important aspect of KYC service providers. It includes regular monitoring of practices of third-party KYC vendors by the fintech firms.
Conclusion
Sectoral sanctions are a powerful tool in addressing global Anti-Money Laundering concerns where OFAC plays a critical role in regulating different industries & sectors to prevent serious criminal activities. KYC & AML solutions provide integral support to enforce sectoral sanctions by aiding the identification of risky customer profiles & transactions. To overcome sectoral sanctions and compliance-related challenges, fintech firms must choose their KYC partners wisely and adopt best practices to ensure robust compliance with sectoral sanctions and evolving regulations.
Visit our KYC Technology Buying Consultancy which assists businesses in carefully choosing the ideal KYC partner, ensuring comprehensive compliance in every aspect.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Sectoral Sanctions
- What is the Sectoral Sanctions Identifications List (SSI)?
- The Role of OFAC in Global Compliance
- The Importance of KYC and AML Compliance
- Risk Mitigation Through KYC AML Guide
- Challenges in Regulatory Compliance
- Best Practices for Effective Compliance
- Conclusion





