Over the last few decades, technology has brought drastic changes in financial industries and adopted digital payment methods. However, these transformations have played a significant role in making international transactions much quicker, cheaper, and more convenient than before. It is anticipated that the amount of cross-border transactions will grow to $39.9 Trillion by 2026, which is crucial in the global economy.
KYC Ongoing monitoring of cross-border transactions is a matter of great concern for governments and regulators. Yet, with the evolving compliance ecosystem, companies desperately seek faster and more affordable methods to get compliant and diminish the burden of KYC demands.
What are Cross Border Transactions?
Cross-border transactions are financial payments, where the financier and the recipient are located in different countries and cover both retail and wholesale transactions along with money orders. Cross-border payments can be made in multiple methods such as credit card payments, bank transfers, and other alternative ways including mobile payments and e-money wallets.
Types of Cross-Border Transactions
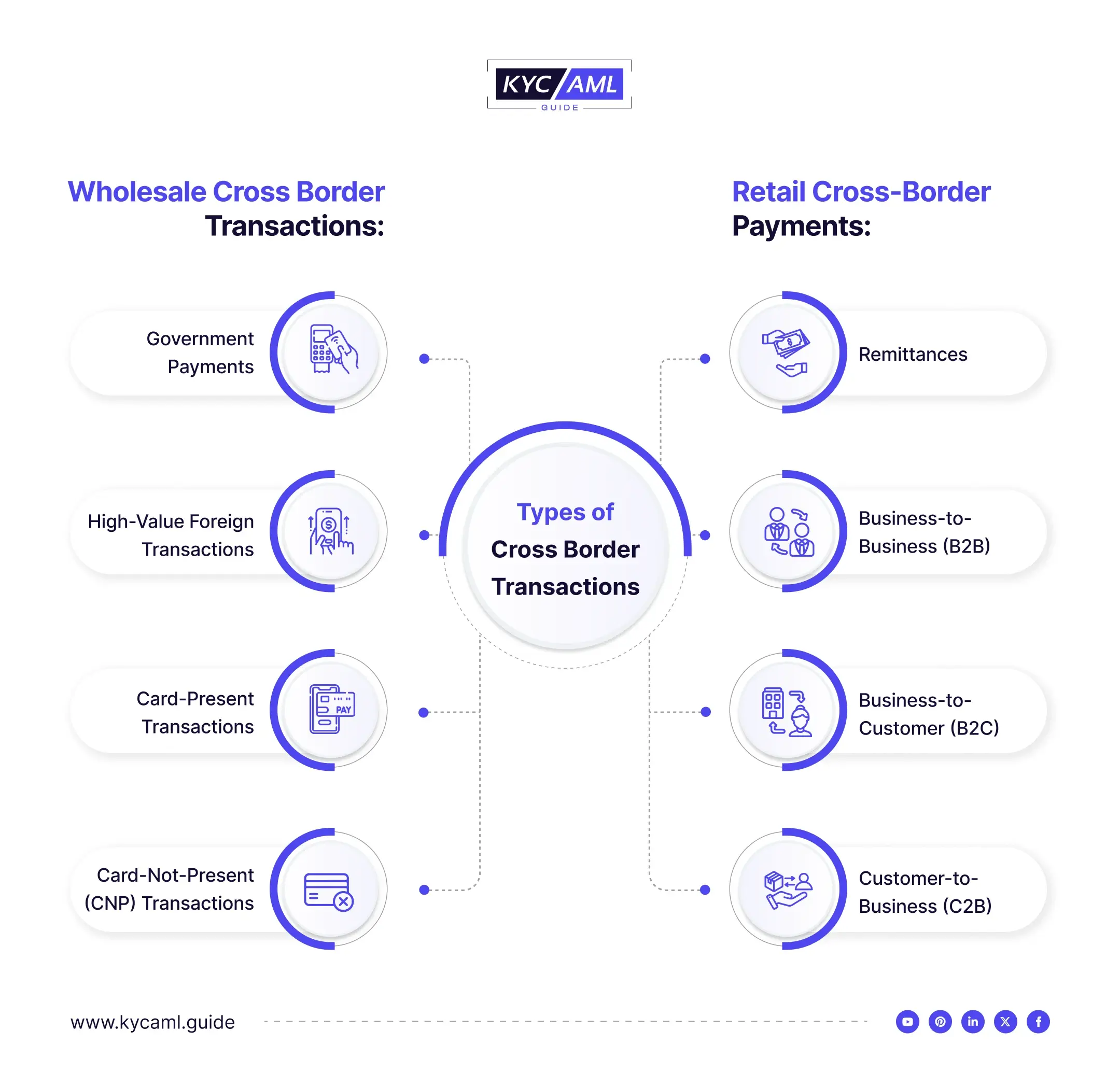
| Wholesale Cross-Border Payments | Retail Cross-Border Payments |
| Government Payments: These include financial aid, custom duties, and other types of financial interactions between governments of different jurisdictions. | Remittances include funds that a foreign national or a traveling person sends to another country, typically to family or friends. |
| Card-Not-Present (CNP) Transactions: These mostly involve international e-commerce platforms like Amazon, etc, and other commercial payments to companies that are established overseas. | Business-to-business (B2B) transactions involve payments between companies across borders and are generally high-value transactions serving their mutual business goals. |
| High-Value Foreign Transactions are related to the purchase of high-value assets such as real estate, art, jewelry, or luxury vehicles in a foreign country. Among these, the movable assets are also delivered to the home country with additional charges. | Business-to-customer (B2C) transactions occur when businesses sell products or services to customers in another country. This can include online platforms and other means of purchase. |
| Card-Present Transactions (CPTs): In this category, travelers use their physical credit or debit cards to make payments abroad. Mostly, tourists and officials traveling for business purposes use CPTs. | Customer-to-Business (C2B): These are transactions where the customer pays a business in another country, usually for services or online purchases. |
Cross-Border Transactions: Challenges & Limitations
Cross-border payments are complex in multiple contexts. In contrast with domestic transactions, customers have to bear huge costs, slower speed, low clarity, and financial security challenges. Additionally, there are several possible challenges that fintech companies face.
i. Low Transaction Speed
In conventional banks, customers have to wait for days to make cross-border transactions. Clients must wait for at least five working days to get their payment done. Moreover, several third parties are also involved in a single transaction process extending the payment processing time.
ii. Financial Security
According to a 2021 report by Global B2B Payments Playbook, almost 60% of UK and US businesses face financial security challenges while carrying out cross-border transactions. This is due to different financial regulators’ lack of coordinated efforts and enforcement actions.
Global cybersecurity regulations are not implemented in every jurisdiction. This makes cross-border payments more vulnerable to cyberattacks in countries with inadequate AML policies or weaker cybersecurity regulations.
iii. Cost Inefficiency
Banks have to collaborate with third-party agents to make payments from one country to another, which is costly. Moreover, integrating different payment methods and technologies also requires investments in fast and secure payment options.
iv. Lack of Transparency
Tracking one’s own cross-border transaction is difficult. You might have to wait for a few days until your bank and the receiver end are notified. As per a survey conducted by EuroFinancy and SWIFT, 47% of cross border clients want these processes to have better transparency. On the other hand, 64% of firms anticipate payment tracking features.
Upholding transparency in cross-border payment processes ensures no hidden charges. Besides, it helps financial organizations recognize errors that might affect their revenue.
Cross-Border Payments in the EU
Regulation (EU) 2021/1230 mandates the customers and suppliers of goods and services to carry out cross-border payments via IBAN (International Banking Number) and BIC (Business Identifier Code). Moreover, the member states are required to:
- Appoint national regulators to regularly monitor cross-border transactions.
- Ensuring cooperation between national authorities especially to resolve cross-border matters.
- Establish complaint procedures for everyone using the payment services.
How KYC Ongoing Monitoring Streamlines Cross-Border Payments?
Timely Detection of Money Laundering and Fraud
and Continuous Monitoring of Transactions helps banks avoid financial crimes in their operations. Whenever a transaction becomes suspicious, an ongoing monitoring mechanism flags it and sends a report to the system for further investigation.
Efficient Banking System
KYC Monitoring of transactions helps banks maintain efficiency and avoid disruptions in their operations in two ways:
- Sort the valid transactions and suspicious ones separately.
- Prioritizing the valid transactions and serving them first.
Enhanced Customer Relationship
Ongoing Monitoring also helps banks improve their customer services by informing them and staying transparent about the importance of KYC practices. Also, banks can educate their customers to use their services properly while staying compliant.
The Role of KYC Solutions in Ongoing Monitoring of Cross-Border Transactions
Cross-border payments require sophisticated ways of identifying customers’ identities alongside the payment service providers’ details. This is to ensure that no cross-border transaction is part of a money laundering scheme. KYC Solutions streamlines the customer onboarding process and conducts ongoing monitoring as a crucial part of risk assessment. But it all links to the identity verification of a customer.
If the customer’s identity is compromised due to poor KYC Checks, the whole process might fail and transactions can either be a theft attempt or serving illicit gains.
Banks and other fintech businesses need to make sure that the KYC Solution implemented is the one with enhanced technologies like Biometric Identity Verification and can monitor transactions in run time with the least possible errors.
KYC AML Guide Helping Cross-Border Payments
We know how important is for banks and other FIs to streamline the monitoring of cross-border payments. This will help in the expansion of their customer base in different countries. So, We provide KYC Technology Buying Consultancy and a KYC Vendor Analysis which are the necessary tools for helping you in selecting the right KYC Tool for ongoing monitoring. Not only this, but we have 24/7 client support to help you every step of the way and help you in achieving regulatory compliance at all times.
Table of Contents
- What are Cross Border Transactions?
- Cross-Border Transactions: Challenges & Limitations
- Cross-Border Payments in the EU
- How KYC Ongoing Monitoring Streamlines Cross-Border Payments?
- The Role of KYC Solutions in Ongoing Monitoring of Cross-Border Transactions
- KYC AML Guide Helping Cross-Border Payments





