What is Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) is a new way of looking at Digital Identities. SSI gives full ownership & control to the individuals and identity holders over their digital identities. It enables you to have full authority over your digital presence and fully decide who can access your information.
It is also known as Decentralized Identity (DID) because it does not rely on third-party centralized identity management to store and manage the identity database.
Here are the 2 definitions by European authorities:
- According to EIDAS (Electronic Identification, Authentication, and Trust Services), Self-Soveriegn Identity should enable users to create their own identity without relying on a centralized authority.
- Christopher Allen in a publication defines SSI as the next step beyond user-centric identity and that means it begins at the same place: the user must be central to the administration of identity.
Before we dive into the exploration of SSIs, let’s look into a brief overview of its parent concept known as digital identity.
What is Digital Identity and Why it is Important?
A Digital Identity is a set of identifiable information about an individual or an entity that exists digitally and is accessible through computers and other digital devices. Digital identity is used for multi-purpose access or sign-up, simplifying the way individuals connect with various online services and platforms.
Digital Identities are of significant importance in the rapidly digitizing world in almost every sector. Here are a few reasons that highlight the importance of Digital Identities:
| Online Authentication | Digital identities serve as the primary means of identity verification & authentication in digital platforms. They allow users to access a wide range of online services, from email and social media to banking and e-commerce. |
| Data Protection | Users can control what information they share and with whom, minimizing privacy risks. It enhances data protection through well-managed digital identities. |
| Interoperability | Various online platforms can access digitally identifiable information and use it to authorize the same customer for their services. |
| Cybersecurity | Through decentralized digital identities unauthorized access, data theft, and cybersecurity issues are reduced to a minimum. |
| User Empowerment | Self Sovereign Identity (SSI) being a vital part of digital identity increases the users’ control over their information. |
What is a Good Digital Identity?
McKinsey defines a good digital identity as having the following 4 characteristics:
- A digital identity has a high degree of assurance in verification and authentication. It meets both government and private sector requirements for registration and accreditation.
- A good digital identity is unique where an individual has only one identity and the system recognizes only one identity for that individual. Today, in most social media platforms, uniqueness is not offered.
- Consent is an important aspect in a good digital identity. It means that the user is fully aware of the use of digital identity and what information will be recorded and shared on the system.
- Data Protection and Privacy are important for a digital identity management system. In-built data security mechanisms ensuring the user’s privacy and protection of personal data and also giving the user full control and access over the information sharing with transparency is what makes a good digital identity.
The Difference Between Federated Identities and SSI
First of all, it is important to know that both Federated Identities and Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) are types of digital identity. Most people today use federated identities that are stored in a centralized database. Federated Identity models offer a Single Sign-On (SSO) option which enables a one-time sign-in to an online service. For example, Google offers SSO where a Gmail account holder can use multiple third-party services from the same Gmail logged-in ID.
Here’s an example of how SSO registration appears in front of the user:
Other examples of platforms that use Federated Identity include:
- Microsoft
- Github
- Amazon
Why SSI?
Since federated ID models are centrally stored and can be accessed by multiple sources the element of user’s control and authority over ID is minimal. Self-Sovereign Identity has enabled a high level of user control over the information and the authority over who to give permission and access or use the identity and information. SSI enhances the level of data privacy and security of information.
Here are the major differences between federated identity and the SSI model:
| Aspect | Federated Identities | Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) |
| Centralized vs. Decentralized Control | They are managed by central authorities or identity providers. Users have a single identity controlled by these entities. | A self-sovereign identity is stored on a decentralized database usually on mobile wallets. Users have control over their DIDs and data. |
| Authentication Process | User authentication often involves redirection to the identity provider’s login page. The identity provider confirms the user’s identity to the relying party. | DIDs use cryptographic methods for authentication, allowing users to prove their identity without revealing personal information. |
| Trust and Interoperability | Trust is established between relying parties and identity providers. Promotes interoperability among services using the same federated identities. The level of trust may vary. | Designed to be interoperable without relying on prior trust relationships, working in a more trust-minimized environment. |
| Privacy and Data Control | User data may be shared with identity providers, potentially raising privacy concerns. Limited control over data management and sharing. | Emphasizes user control and privacy. Users have autonomy over personal data and can choose what to share and with whom. |
| Use Cases | It is commonly used in scenarios requiring seamless login experiences across multiple services or organizations. (e.g., single sign-on solutions) | Applied in contexts where users must maintain control over their identity, especially in trustless interactions, blockchain-based identity, and privacy-focused use cases. |
This information shows that SSI is majorly used due to enhanced privacy and user control over identities.
How does Self-Sovereign Identity Work?
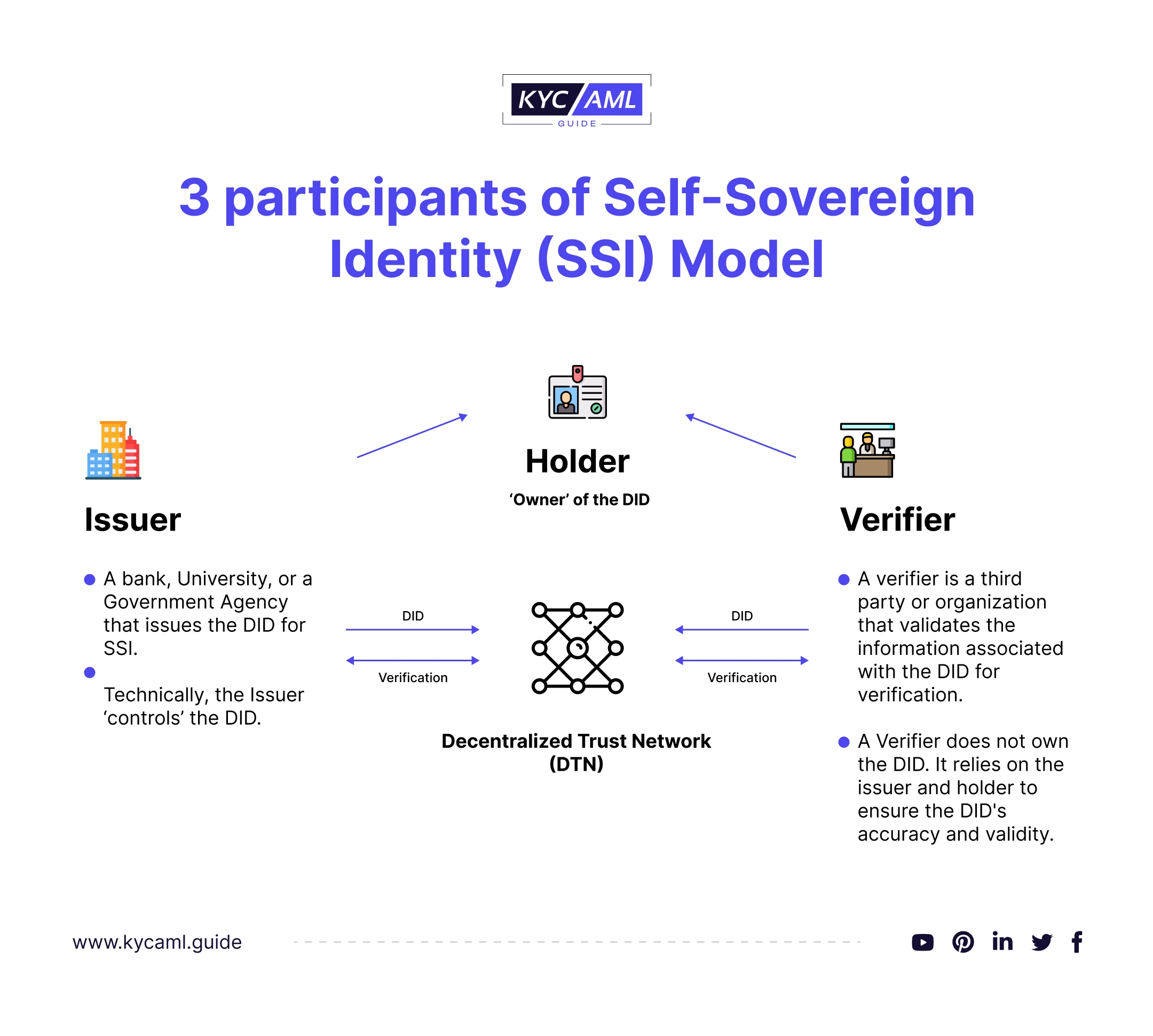
As mentioned earlier, The SSI stores identifiable information on a decentralized database. It is also called a decentralized identifier or DID. There are 3 participants in the SSI model:
- Issuer: A bank, University, or a government agency that issues the DID for SSI. Technically, the Issuer ‘owns’ the DID.
- Holder: An individual whose DID is being issued or simply ‘controls’ DID and possesses it. A holder receives verifiable credentials from the Issuer to access the service.
- Verifier: A verifier is a third party or organization that validates the information associated with the DID, typically for authentication or verification purposes. A Verifier does not own the DID. It relies on the issuer and holder to ensure the DID’s accuracy and validity.
Why SSI is Trustworthy?
A high level of confidentiality and data security is ensured through different tactics in SSI. From Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) to Decentralized Trust Networks (DTNs) this identification model ensures that information is shared only when the user allows it. The DTN maintains secret records of DIDs and Verifications between the Issuer and verifier and guarantees the Holder a high level of privacy and security.
To put it in easy terms, the SSI model is based on 3 pillars:
- Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) enable users to prove their identity through a unique code stored on the mobile wallet database.
- Blockchain is used as the decentralized storage of identities making it difficult for hackers to access the database.
- Verifiable Credentials are crafted through cryptography making them uniquely secure for users.
SSI being decentralized offers data protection because when the identifiable information is stored on different servers connected to the blockchain, failure in one system won’t affect the database due to backup and multiple nodes.
Use Cases of Self-Sovereign Identity
SSI has multiple use cases in different industries. For example,
1) KYC (Know Your Customer)
The KYC Onboarding Process can be streamlined with the use of SSIs as the user is empowered to sign up without the need for a third-party Vendor. Users can now directly upload their information on the decentralized network where banks, FIs, and crypto exchanges can only access the users’ information upon their permission. 90% of cost reduction is predicted in customer onboarding due to the use of Digital Identities as per McKinsey. This shows potential growth in the use of SSIs as a new way to onboard customers.
Also read: What is eKYC (Digital KYC)?
2) NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens)
NFTs created through SSI can help prove the actual identity of the creator and owner of the NFTs as long as they exist. SSI enables owners to prove their identities without connecting to Mining platforms like Ethereum, or Smart Contracts.
3) Healthcare
Patients’ accurate identities and medical history can be efficiently recorded through SSI which can be securely accessed by multiple services alongside the element of privacy with patients’ control over their personal medical information.
4) Proof of Income
SSI can help streamline financial information sharing about users and prevent fraudulent claims in any of the financial services.
5) Education
Universities can use SSI to manage the students’ information for multiple uses like Student onboarding, student foreign exchange, and other education services. Students can store their educational records in their digital wallets through SSI.
Challenges and Threats in the Self-Sovereign Identity
| Aspect | Challenges & Threats |
| Global Acceptance | Individuals, governments & entities need to embrace the Self-Sovereign Identity models collectively for its successful implementation. This may take years to switch over SSI from federated and centralized ID systems. |
| Misuse of Identity | Another challenge in SSI is the misuse of identities as the user fully controls personal information sharing. The user can misuse this control to engage in different illicit and fraudulent activities. |
| Technological Limitations | Certain groups may be left behind due to limited access to resources and technologies that are used to implement SSI. this may create disparities or worsen them for existing outdated systems. This requires full system upgradation and may cost more than the organization’s budget. |
| Interoperability | Due to a trust-minimized decentralized blockchain interoperability is a critical challenge in Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) systems. SSI allows individuals to have control over their digital identities, but it also means that there are multiple, often independent identity providers. Achieving interoperability among these various SSI systems is essential to ensure that digital identities can be universally recognized and accepted. Without interoperability standards and protocols, individuals might face difficulties using their SSI credentials across different services, organizations, or platforms. |
| Lack of Regulatory Framework | Federated Identity Management Systems and other traditional IDV systems are regulated by established regulatory bodies. Unlike these IDVs SSIs are still awaiting regulations which can cause legal recourse in case of fraud or non-compliance. Also, non-regulated SSI can easily be compromised and legal actions against them are difficult. |
| Privacy & Consent | Self-sovereign identity raises an underlying concern about data privacy & consent as the data is shared among different parties over the decentralized network. To establish trust and Verification, information-sharing can cause unintentional sharing of sensitive information over the internet. |
| Discrimination & Exclusion | Not everyone has equal access to the data stored. SSI is intended to empower users with their personally identifiable information and privacy. However, limited to no access to technologies necessary for SSI can be a limitation—also, SSI stores data provided by individuals which may create an issue of bias and discrimination. This may result in discriminatory onboarding, hiring, and lending decisions that can occur based on SSI credentials. |
The Future of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
So far, federated identities are coexisting with SSIs in the digital identity zone but financial institutions have started switching to SSIs as the new face of identity verification. Various factors have contributed to driving this shift from centralized federated identities to decentralized SSIs.
Economic Value
Mckinsey’s focused jurisdictions for the economic value through digital identities are as follows:
- The United Kingdom
- The United States
- China
- India
- Nigeria
- Brazil
- Ethiopia
- China
There are four major areas where digital identities can create value by 2030 for these jurisdictions.
| Increased Employment | Digital Talent Matching has increased labor force participation with Nigeria being on top. |
| Cost Savings (contribution to GDP) | Savings from the sharing of medical information through digital identities have increased with the US being on top. |
| Increased percentage of total wages & benefits | Payroll fraud has been reduced with Nigeria on top resulting in cost savings in wages and benefits. |
| Time savings in e-government services | Overall efficiency in government-related services has increased and China is on top among the focused jurisdictions. |
Overall, countries that implement Digital ID can experience an increase in GDP equivalent value of 3 to 13% by 2030.
Value for Individuals
Exhibit 11 in McKinsey’s report reveals that through different interactions with digital identities, individuals can gain nearly 50% of the potential value of digital IDs in the focused countries.
- Brazil spent 38% of its GDP on benefits. With Digital IDs, Brazilian taxpayers can save up to $90 billion while eliminating ghost beneficiaries & leakages in the public benefits system.
- 81% of the Nigerian workforce is self-employed. Digital Identities can save up to $350 million by eliminating ghost workers. It can also accrue an additional $3 billion on public welfare programs.
W3C’s Recommendation of DIDs (Decentralized Identifiers)
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) invested in DIDs and Verifiable Credentials for a more decentralized, consent-based & privacy-oriented data-sharing ecosystem. For this purpose, it announced Decentralized Identifiers as an official Web standard in July 2022. Different sectors are in the process of adopting these standards such as:
- The governments of Canada, the EU, and the US are exploring the use of DIDs to resolve the privacy concerns of entities.
- Retailers including grocery stores, restaurants, and bars are using DIDs for increased checkout speed, to prevent fraud while purchasing age-rated products, and to increase privacy.
- Workforce use cases include universities, job training programs, and education standards organizations that issue digital learning credentials that are controlled and shared by the graduate when applying for higher education or workforce positions.
W3C Recommendations stress the importance of DIDs as a whole. Self-sovereign DIDs being part of DIDs can be introduced to embrace the principles of user-centric control over digital identity, offering enhanced security and privacy.
Identity Solution Providers & SSI
Identity Solution providers are focusing on introducing Self-Sovereign Identity for different sectors. Identity Verification is a crucial part of many businesses at the forefront of their financial security and regulatory compliance. For this purpose choosing the right Identity Verification Solution Provider that offers an SSI model ensures privacy and control to the users. Utilize the KYC AML Guide to empower your decision-making process and identify the perfect KYC Identification Solution Provider with the assistance of our specialized KYC Technology Buying Consultancy.
Final Thoughts
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) is a trending concept in empowering individuals with full control over their own identity and personal data, eliminating the need for centralized authorities or intermediaries on the frontline. Governments and Regulators must explore the potential of SSIs in ID verification but also look into the threats and challenges in its global implementation.
Table of Contents
- What is Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
- What is Digital Identity and Why it is Important?
- The Difference Between Federated Identities and SSI
- How does Self-Sovereign Identity Work?
- Use Cases of Self-Sovereign Identity
- Challenges and Threats in the Self-Sovereign Identity
- The Future of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
- Identity Solution Providers & SSI
- Final Thoughts





