Researchers have predicted a CAGR of 13.9% in the NFC (Near Field Communication) market by 2032. Valued at US$ 24.8 Billion in 2022, the projected growth of the NFC market is also expected to be positive during the growth period. A 30-year-old technology is back in business as the COVID-19 pandemic and other factors lead to the need for a touchless and short-distance data verification technology.
NFC (Near Field Communication)
NFC is an old technology yet its benefits are being exposed to the world today. Initially, NFC chips were used for limited services like payments of ticketing. Now their use cases have encompassed a vast array of applications in daily life. One of these use cases is e-passports having NFC chips installed usually on the cover. This small chip with a size at least three times smaller than a Canadian penny stored all the necessary identifiable information about the passport holder. This passport can be read through NFC-enabled scanning devices including the smartphones that are NFC-enabled. It requires a few centimeters of distance between the NFC-enabled device and the chip.
Benefits of NFC e-Passport Verification
| Contactless |
|
| Time-Saving |
|
| Cost-saving |
|
| Highly Accurate |
|
How does NFC e-passport Verification work?
The NFC chip is usually located on the front or back cover page of the passport. The scanning device uses RFID technology to read the NFC chip from the passport which is placed at a distance of 4cm at maximum from the scanner. Here’s how NFC Passport verification works.
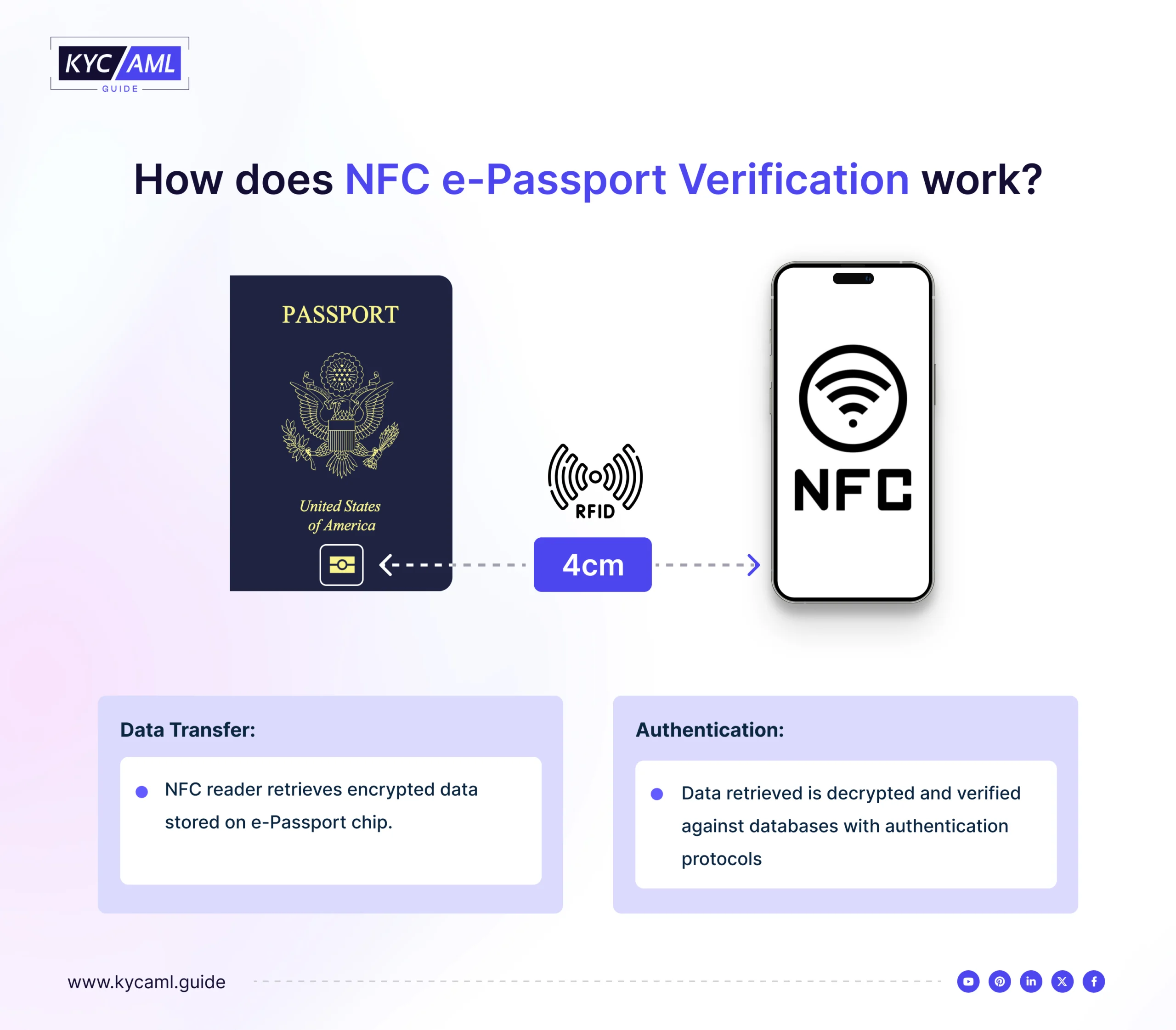
- Passport with NFC Chip: The passport contains an embedded NFC chip that stores the passport holder’s information securely. This chip is typically located on one of the passport pages.
- NFC-Enabled Device: The device used for verification, such as a smartphone, tablet, or specialized NFC reader, must also have NFC capabilities. Most modern smartphones are NFC-enabled.
- Physical Proximity: To initiate the verification process, the NFC-enabled device needs to be brought into proximity (usually within a few centimeters) to the NFC chip in the passport.
- Data Transfer: Once the devices are in proximity, the NFC chip in the passport communicates with the NFC reader in the device. The reader retrieves the encrypted data stored on the passport chip.
- Authentication: The data retrieved from the passport chip is then decrypted and verified against databases or authentication protocols to confirm the passport’s authenticity and the identity of the passport holder.
Also Read: KYC Document Verification
How NFC e-Passport Verification will evolve in the near future?
As of 2021, more than 100 countries have successfully implemented NFC passport verification. While claiming that it is a contactless and secure means of customer identification, it poses some challenges and has limitations to its use. Here is an overview of the challenges and limitations of using NFC verification for passports.
- NFC Passport verification is still insecure if the passport is lost or stolen. It can be misused to travel with data manipulation or impersonating the data present on the NFC chip.
- NFC Device compatibility is another issue. Not all smartphones and devices are NFC enabled. While most modern smartphones have NFC capabilities, there may still be some older models or specialized devices that need this feature. This limitation could hinder the widespread adoption of NFC passport verification, particularly in regions where access to compatible devices is limited.
- Interoperability is another major concern for the future of NFC-enabled devices. Standards for NFC passport technology may vary between countries, leading to compatibility issues and potential difficulties in implementing cross-border verification processes.
- NFC Technology may become obsolete in the coming years. It is because of the increasing use of AI-driven technologies which are pushing the need for a seamless and remote verification of users. The same concept applies to NFC Passports.
Wrap Up
NFC e-passport verification is a widespread technology in multiple countries. However, it may not be a part of the futuristic approach as emerging technologies including biometrics and AI are enabling banks and FIs to shift to a more sophisticated, accurate, and seamless mechanism for identity verification. Passports can now be stored digitally in digital wallets which can be accessed by airlines and other verifying authorities. However, many jurisdictions are still in the process of shifting to NFC passport verification. Despite its limitations, NFC technology serves as the foundation for newly introduced identification systems where NFC verification with integration of biometric authentication can enhance security levels and make it difficult for bad actors.





