Difference between MRZ Code vs QR code
MRZ Code
The MRZ code is an important part of the passport. It allows machines to read and verify identity documents and information. The MRZ code is in the identity document. Most IDs have 3 MRZ lines and 30 characters, passports have 2 lines of 44 characters each. The aim is to facilitate the automatic analysis of information about the document holder, such as
- First name,
- last name,
- Document number,
- Country,
- Date of birth and
- The validity period of the document or expiry data
Today, the MRZ can be found on the photo page of every international passport, along with various forms of identity documents such as visas, residence permits, and more. A document with an MRZ code is called an MRTD (Machine Readable Travel Document).
MRZ code example
A common MRZ code in a passport is as follows:
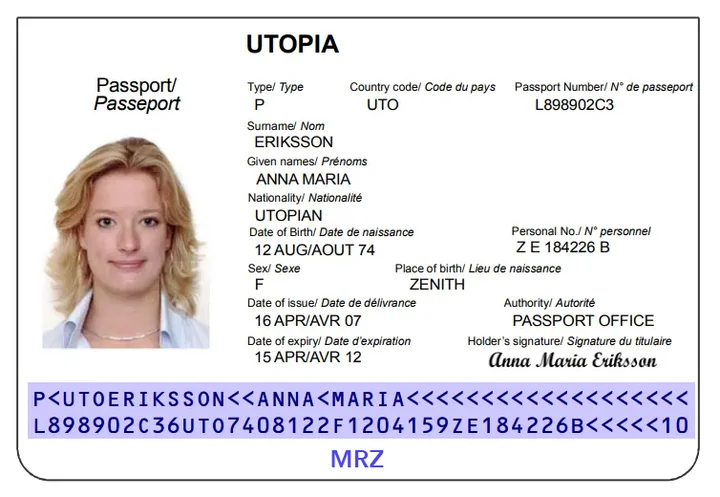
In this example:
| First Row | Document type (P for passport), Country code (UTO for the unknown country), First name (ANNA MARIA), Last name (ERIKSSON), and padding characters. |
| Second Row | Document number (L898902C<3) Nationality (UTO) Date of birth (690806) Gender (1 for women) Date of expiry (F940623) Individual number (6ZE184226B<<<<< 10) |
QR Code
A QR code is a series of black-and-white pixels or squares in a grid that stores machine-readable data. The information in the QR code is quickly processed by the smartphone or camera. The QR code has a pixel format, making it a convenient way to store and access data. Data stored in a QR code can include a phone number, website URL, or text up to 4,000 characters.
QR authentication is a digital password system that uses QR codes as a passport to access websites or applications. To generate QR codes for login the online platform uses in-app QR code software. Once they appear on your desktop, use your phone to scan these codes for instant identity verification for example to login to Web Whatsapp. This means you no longer need to enter or remember complex. To verify and access your data one scan is enough.
Example of QR Code
QR codes can carry various data. Here’s an example of a QR code with a website URL:
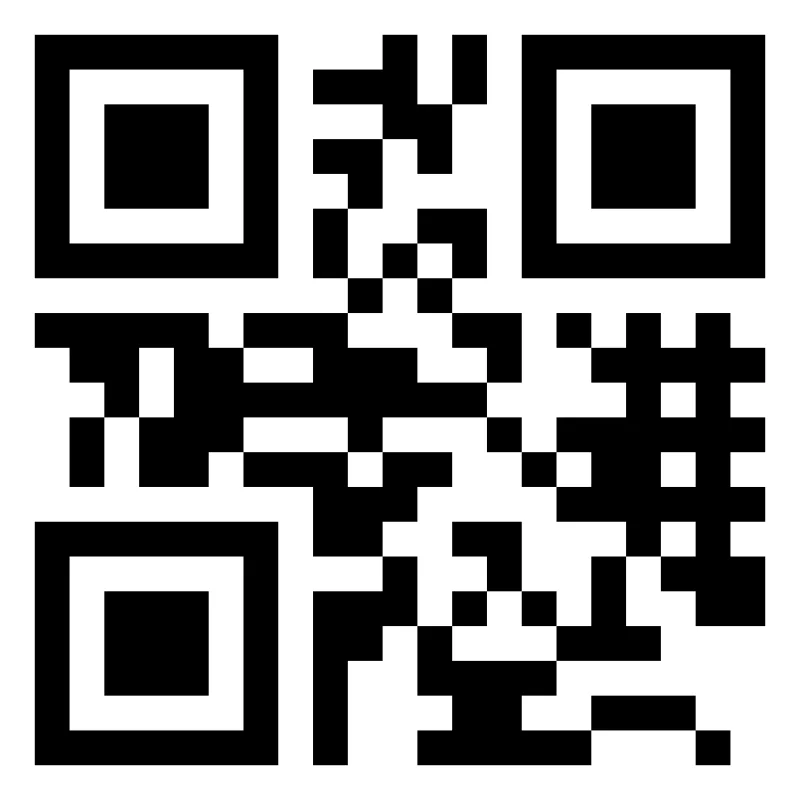

The smart camera scans the QR code and directs the user to “https://example.com”.
Please note that the content and format of MRZ codes and QR codes may vary depending on the application and intended security or communication method.

How to Expedite the Verification Process?
MRZ’s role in identity verification cannot be overlooked. Today, it is easier for authorities to verify and identify most passports and identity documents due to machine-readable zones. During background checks, passport verification is a standard procedure. MRZ passports have successfully verified suspicious identities as the MRZ code contains all the important data about a person as mentioned above.
Companies can easily conduct identity verification with an MRZ-based personal identification document. However, getting the most out of the MRZ code requires robust MRZ identification technology that can speed up the verification process.
QR codes allow companies to integrate two-factor or multi-factor authentication into existing systems, allowing all their users to authenticate through a QR code-generated OTP. OTPs are always unique and have a time limit. So every time a user visits a page or uses a service a new OTP will be generated to verify the identity for example when you are doing a transaction from your mobile application an OTP is sent to your registered number to verify your identity.
You can also use QR codes to save documents having QR codes on them. You simply scan the code with your mobile device and access the system where the information is stored. This allows instant identity verification of the document against information from a trusted database. If the information is correct, you can be sure that the document is genuine.
Are QR Codes Safe?
Since QR codes cannot be read by humans, attackers can easily modify QR codes to point to other sources without being detected. Attackers can insert malicious URLs containing customized malware into QR codes, which after scanning can collect data from mobile devices. It’s also possible to enter malicious URLs and QR codes that redirect to phishing sites where unsuspecting users can reveal personal or financial information. In addition to opening a website, these actions may include adding contacts or writing emails. As QR codes can be scanned by mobile devices, they are no more secure than computers or laptops and increase the potential risk.
Pros and Cons of MRZ code: MRZ Code: Enhancing Travel Security and Efficiency
- MRZ codes improve the authentication process as they are designed to be machine-readable quickly.
- MRZ ensures that personal information is properly stored and verified. It reduces the risk of fraud or identity theft.
- It is a cost-effective identity verification solution. The code can be perused by various devices, including mobile devices and web browsers
- MRZ code are accurate and it reduces the inaccuracy of personal data.
- The chances of human error are less due to computer-generated code.
However, there are some drawbacks as well:
- MRZ code may contain inaccuracies, human errors, and mechanical errors even with automated verification.
- The main issue in MRZ code is Data security and privacy. As MRZ code records individual data in the system the hackers can illicitly acquire these identities to commit fraud or identity theft.
Bottom line
In short, QR code and MRZ code if implemented correctly and used in the right way can be used for security. The security of any type of code depends on factors such as the nature of the data entered, measures taken to protect against illegal access or manipulation, and the overall security of the system or document using the code. When evaluating the security of a QR code or MRZ code, it is important to consider the use case and security measures. Both have their pros and cons, the best identity verification technique for your business is that which fulfills your objectives. KYC AML guide a research-based consultancy can help you by offering KYC technology buying that can help you to choose the best identity verification solution.