Background of PSD2
It is the second update of Payment Service Directive that was adapted in 2015 by the European Union. It’s primary regulatory authority is the European Commission. PSD2 establishes the regulatory framework for the retail payments for all euro, non-euro and cross-border payments. It is a replacement of the first Directive (PSD) that was issued in 2007.
Purpose of PSD2
The prime focus of PSD2 compliance was to prevent Payment Fraud and to streamline and regulate the payments industry in European and Non-European payments. It also focuses on the protection of consumer rights who utilize the payment services.
Sections of PSD2
There are two main sections in PSD2:
1 Market Rules
These are the instructions that set boundaries for which type of organizations can provide payment services. Mainly, they include banks, central banks & government bodies. Two special organizations are also included: Electronis Money Institutions (EMIs) and Payment Institutions (PIs).
2 Business Conduct Rules
These are the guidelines for the payment service providers for information sharing with general public. This information includes disclosing the payment services charges, the exchange rates that service providers use, the reference numbers for transactions, and the longest time it could take for a transaction to be done.
Proposed Changes to the Payment Service Providers through PSD2 Compliance
Payment Service Directive aims at achieving the following:
- Increased efficiency and transparency while chosing payment services for consumers and merchants
- Bring innovation in payment services for expanding the market reach
- Ensuring a high level of protection for payment service users across all Member States of the EU
After the evaluation took place with advice by the EBA (European Banking Authority) in 2022, the proposed changes by the EC are as follows:
- Improve the fight against Payment Fraud
- Permission to Non-bank Payment Service Providers to access the EU payment systems.
- Improve the functionality of Open Banking
- Ensuring the Consumer Information & rights
- Ensuring availability of cash
- Shifting the legal frameworks on e-money & e-payment systems
Importance of Electronic Payments
Referring to the ECs Retail Payment Strategy, good and efficient systems for making payments in stores or online are vitally important for the European Economy to flourish. These systems help people easily buy and sell things between themselves. They’re also important for the EU in independent decision-making. The way Europeans pay for things has been changing a lot lately, with new ways like tapping cards and super-fast transfers.
Key findings in the PSD2 Evalutation 2022 by the European Commission (EC)
The Evaluation of PSD2 by EC concluded that it achieved its goals successfully in varying degrees for different types of payment services and areas of the financial industry.
1 Fraud Prevention
With the introduction of the requirement of Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) by PSD2, it helped in fraud mitigation across the Member States. It is estimated in a report that roughly €900 billion was saved by consumers in fraud losses due to PSD2’s improved customer protection measures. It is to be noted that this estimate is a number researched by the linked source. Exact numbers are yet to be researched & revealed.
2 Customer Service
On the other hand, customers felt difficulty due to the implementation of SCA requirement. Also, few loopholes were identified in the SCA that gave a way out to the fraudster to bypass the PSD2. Further improvements in ongoing monitoring of the system was suggested.
The EC’s Approach to Prevent Payment Fraud
The commission if giving ‘Fraud Prevention’ utmost importance under PSD2 compliance. It believes that any updates in the PSD must contribute towards fraud mitigation and prevention. New fraud tactics have surfaced that PSD2 is not adequately equipped to counteract. Here the need of another update PSD3 is felt and The EC has published proposals for it. SCA falls short in fighting new fraud tactics like ‘Spoofing’. So, to prevent payment fraud following preventive measures were proposed:
- To expand IBAN/name matching checks to all credit transfers, as proposed by the EC for Euro instant payments. This will benefit consumers for both regular and instant transfers.
- To establish a legal foundation for Payment Service Providers (PSPs) to share fraud information while following GDPR rules, using specialized IT platforms.
- To reinforce transaction monitoring for enhanced security.
- Requiring PSPs to educate their customers and staff about payment fraud to raise awareness.
- To extend consumer refund rights in specific scenarios.
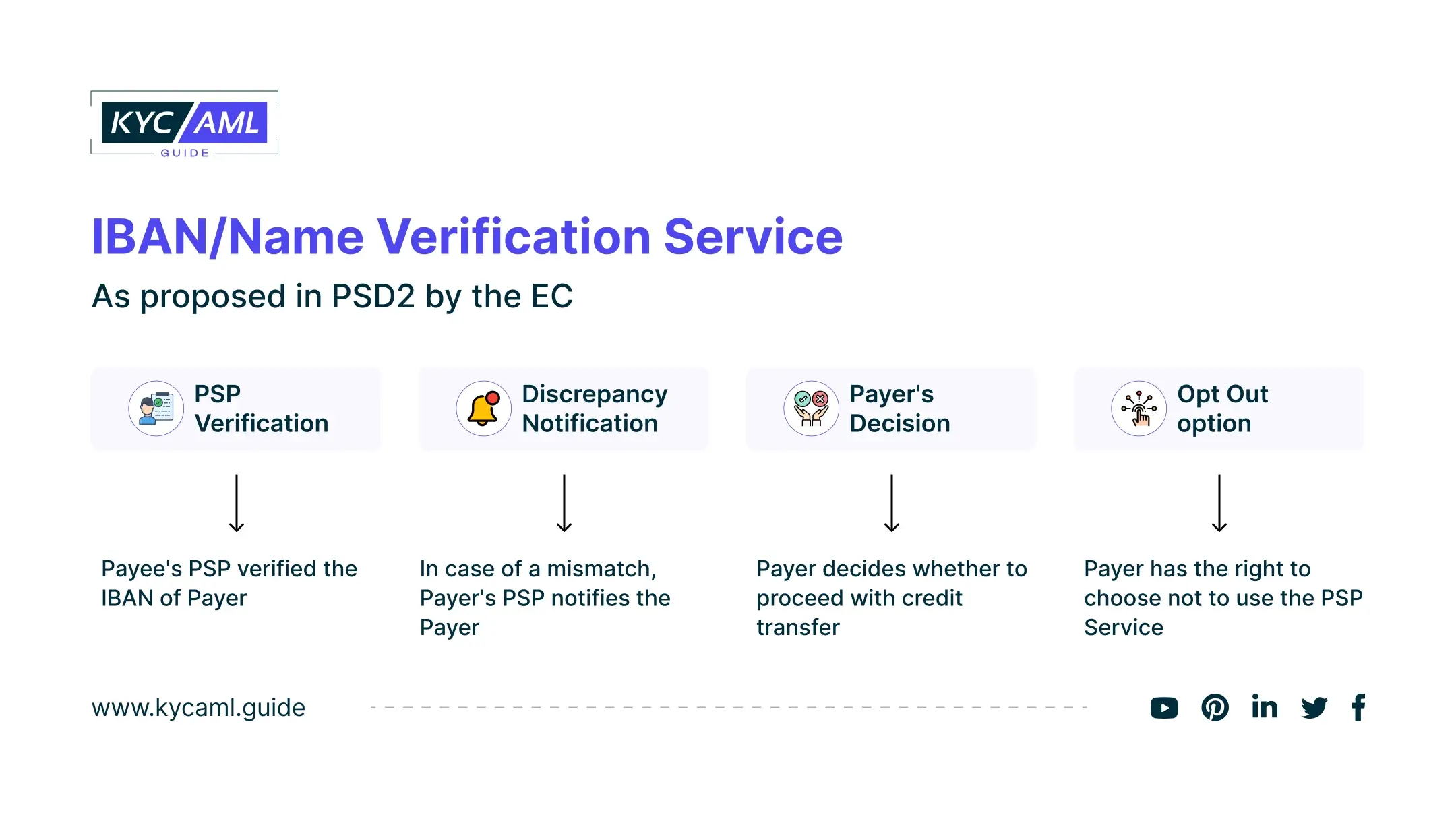
Working of the New IBAN/Name Verification Service
PSD2 and Open Banking
Open Banking refers to the information sharing between banks & third-party service providers. It is mainly done through Application Programming Interface (APIs). As per the European Commission, Open Banking is defined as:
The process by which Account Information Service Providers (AISPs) and Payment Initiation Service Providers (PISPs) jointly or separately enable third parties to offer Value Added Services (VAS) through information & data sharing.
Open Banking existed well before PSD but in a non-regulated environment. PSD provided Open Banking with a regulated framework and enhanced the security while information sharing. After PSD implementation, banks are obligated to teh access of payments for both AISPs and PISPs.
Impact of PSD2 Evaluation 2022 on Payment Service Market
| Impact | Related Concerns & Proposed Points | |
| 1 | Payment institutions and e-money institutions (PIs and EMIs) have grown in numbers and importance since the enforcement of PSD2. |
|
| 2 | Banks will face stricter rules when providing account services to non-bank PSPs, including stronger requirements to explain access denial and service withdrawal. |
|
| 3 | Existing regulatory framework for e-Money is found out to be reasonably consistent. (See e-Money Directive) |
|
Furthermore, the European Commission proposed the following key points under PSD2 Compliance:
- Requirement for a secure framework for Financial Data Access
- Effective Access to Customer Data
- Enhancing Customer Trust
- Aligning PSD2 with other Regulatory Frameworks such as Data Governance Act, Digital Markets Act, and Data Act proposal and GDPR.
- Subsidiarity Principle
- Compensation for Data Access
Also Read: Data Protection Act | KYC AML Guide
Wrap Up
Payment Service Directive (PSD) is a legislation to regulate the Payment Service Industry in the Member States of EU and beyond. Proposed updates in the PSD2 and PSD3 focus on combatting the newer fraud tactics and recognize the importance of stricter Identification and verification mechanism for Payment Service Providers. Moreover, a robust KYC system can help the non-bank PSPs in staying PSD2 compliant. As customer onboarding, transaction monitoring and due diligence being the core elements of a KYC system will ensure secure payment transfers and detection of fraud.
Also Read: How AI-powered ID Verification Combats Digital Fraud
Table of Contents
- Background of PSD2
- Proposed Changes to the Payment Service Providers through PSD2 Compliance
- Importance of Electronic Payments
- Key findings in the PSD2 Evalutation 2022 by the European Commission (EC)
- The EC’s Approach to Prevent Payment Fraud
- PSD2 and Open Banking
- Impact of PSD2 Evaluation 2022 on Payment Service Market
- Wrap Up





